Recent advances in 3D printing for floating drug delivery platforms
Floating drug delivery is a gastro-retentive delivery system offering an advantage for poor-bioavailability drugs, which have low absorption in the upper gastrointestinal tract. This system can be administered effectively, increasing bioavailability and optimizing absorption. This technique can also prolong drug release, resulting in less frequent drug administration throughout the day. However, key restrictions of floating drug delivery are the ability to change drug dosage, drug release kinetics, buoyant force, and duration to suit each patient. With the constraints of the conventional manufacturing process, 3D printing has been developed to produce floating drug delivery devices with flexible dosage forms. This review summarizes studies that used different 3D printing techniques and materials to produce their own floating drug delivery systems and also discuss the limitation of this manufacturing technique.
List of polymers and their properties applied to produce a 3D printing model for floating drug delivery systems:
| Printing technique | Printing material | Printing material properties and preparation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
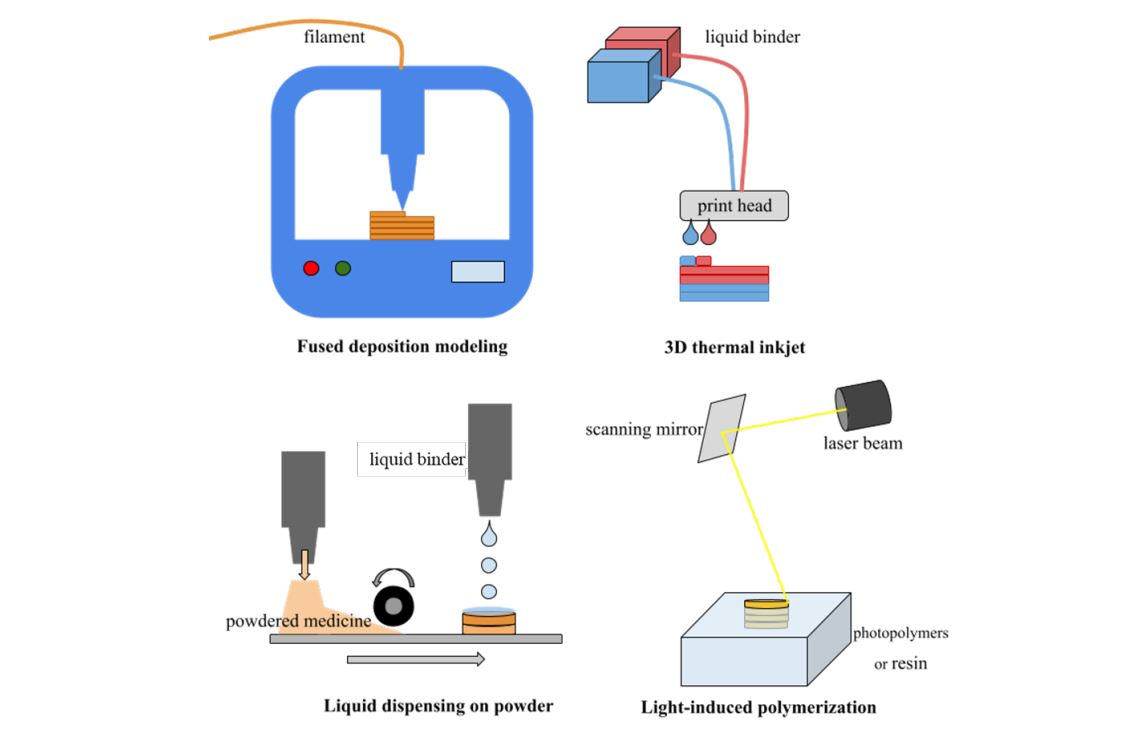
| FDM | hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) | HPMC is a nonionic thermoplastic polymer. HPMC, together with the drug, can be melted and prepared as filament before being used in the 3D printing process. | Giri et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2021 |
| FDM | hydroxypropyl cellulose(HPC) and polyvinylpyrrolidone vinylacetate (PVA/VA) copolymer | HPC is a nonionic thermoplastic cellulose derivative. PVP/VA are also thermoplastic copolymers. They can be melted with the drug and treated as filament before being employed in the 3D printing process. | Vo et al., 2020 |
| Pressure-assisted microsyringe | hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPMC), microcrystallinecellulose (MCC), and lactose | All of these ingredients including drug can be combined to make a slurry. Then they were printed and dried in the position specified by the 3D model. | Wen et al., 2019 |
| FDM | polylactic acid (PLA) | PLA is a synthetic biodegradable polymer that is insoluble. It's a thermoplastic polymer with a high strength and modulus. PLA may persist up to 3h in acid, making it ideal for drugs that need to be released slowly. | Fu et al., 2018 |
| FDM | Soluplus® | Soluplus® is a polymeric solubilizer with an amphiphilic chemical structure. It is a graft copolymer composed of polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl acetate, and polyvinyl caprolactam. It is suitable for hot-melt extrusion because of its Tg of about 70°C and low hygroscopicity. | Hardung et al., 2010 |
Download the full review as PDF here Recent advances in 3D printing for floating drug delivery platforms
or read it here
Sriamornsak, P., Huanbutta, K., and Sangnim, T. (2022). Recent advances in 3D printing for floating drug delivery platforms. Science, Engineering and Health Studies, 16, 22010001.

