Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds
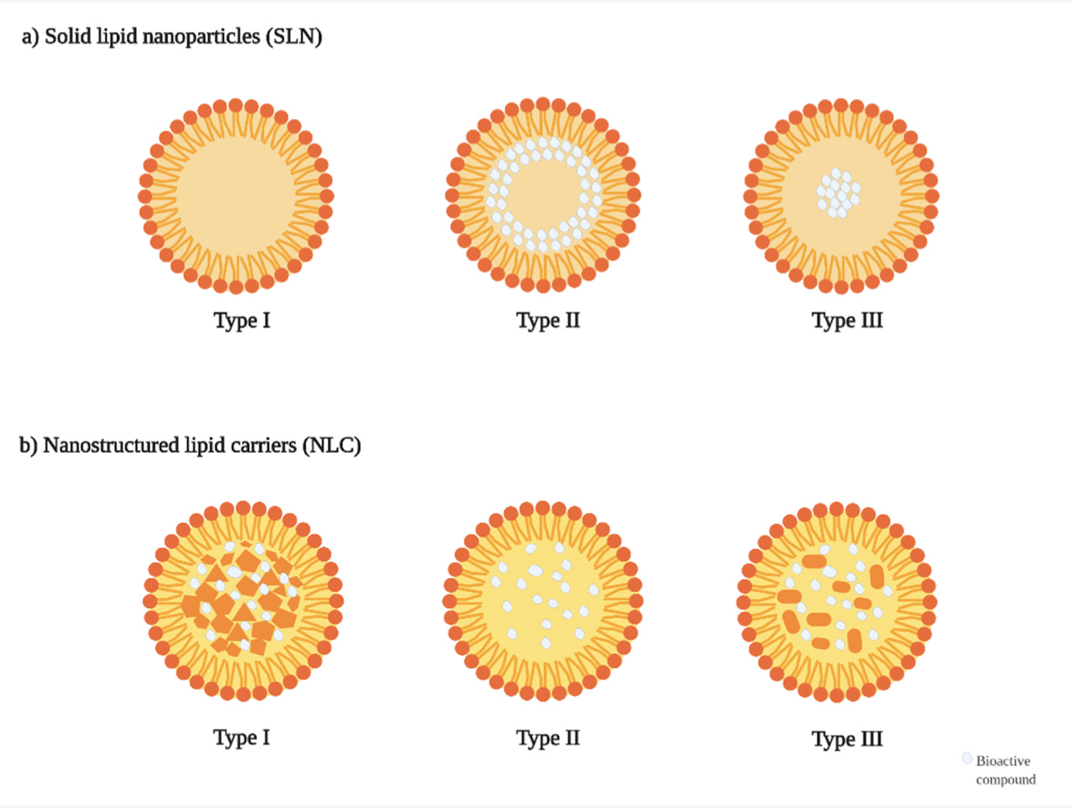
Phenolic compounds are one of the most widespread classes of compounds in nature, with several beneficial biological effects being associated with their anti-oxidant and anti-carcinogenic activities. Their application in the prevention or treatment of numerous chronic diseases have been studied, but a major drawback is still the low bioavailability of these compounds, as well as their instability towards pH, temperature, and light in some cases. Nanotechnology has emerged as an alternative to overcome these limitations, and the use of lipidic encapsulation systems is a promising technique to achieve an efficient drug delivery, protecting molecules from external factors and improving their bioavailability. In this review, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers are highlighted as an important tool for the improvement of the bioavailability and stability of natural phenolic compounds, including their preparation methods and functionalization approaches and the discussion of several applications for putative use in cosmetic and pharmacologic products.
Download the full publication here: Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds
or continue reading here: Borges, A.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998.
Examples of solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) applications, lipids, and surfactants used in their preparation (from this publication)
| Lipid Nanoparticle | Incorporated Molecule | Lipids | Surfactants | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLN | Vitamin E | Precirol ATO 5 | Tween 80 | Skin applications |
| SLN | Quercetin | Glyceryl monostearate (GMS) | Tween 80 and polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400 | Food applications |
| SLN | Baicalen | Tripalmitin, Gelucire 48/9, and Gelucire 62/5 | Poloxamer 188 | Treatment of ischemic stroke |
| SLN | Apomorphine hydrochloride | Tripalmitin, hydrogenated soybean phosphatidylcholine (HSPC), glyceryl monostearate (GMS), and polyethylene glycol monostearate (PMS) | Pluronic F68, L-ascorbic acid | Treatment of Parkinson’s disease |
| SLN | Tetandrine | Compritol 888 ATO | Myrj 52 | Treatment of ocular diseases |
| SLN | Ofloxacin | Palmitic acid | Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Improvement of pharmacological activity |
| NLC | Curcumin | Precirol ATO 5 and Miglyol 812 | Lutrol F68 and Tween 80 | Intraperitoneal administration |
| NLC | Calcipotriol, methotrexate | Precirol ATO 5, squalene mixture, Myverol 18-04K | Pluronic F68 | Treatment of psoriasis |
| NLC | Paclitaxel | Glyceryl monostearate (GMS), soya lecithin, soybean oil | Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) | Cancer targeting |
| NLC | mTHPC (commercial formulation Foscan) | Soybean oil and Suppocire NB | Lipoid S75, Myrj S40 | Photodynamic therapy |
| NLC | Mediterranean essential oils | Labrafil, Softisan 100 | Kolliphor RH40, Tween 80 | Treatment of Candida skin infections |
Keywords: solid lipid nanoparticles; nanostructured lipid carriers; phenolic compounds; bioactivity; chemical stabilization

