Chitosan/poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) films for ocular drug delivery: formulation, miscibility, in vitro and in vivo studies
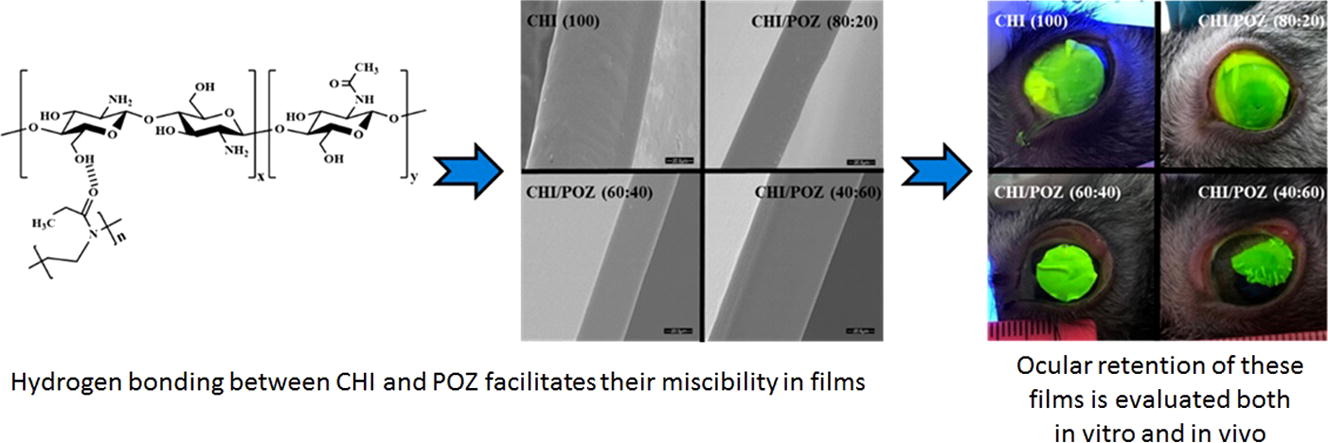
Polymeric films were prepared based on chitosan and its blends with poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) by casting from aqueous solutions. These materials were characterised using a number of physicochemical techniques, including Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermal gravimetric analysis, differential scanning calorimetry, wide angle x-ray diffraction, tensile testing and scanning electron microscopy.
All these studies indicate that there is a weak intermacromolecular hydrogen bonding between these polymers, which facilitates their complete miscibility in solid state. These films were formulated with sodium fluorescein as a model drug and were evaluated for their potential application in ocular drug delivery both in vitro and in vivo. It was established that the films are biocompatible and mucoadhesive; they are capable of providing a sustained drug release when administered topically on the cornea.
Read more about Chitosan films for ocular drug delivery
Article Information: Chitosan/poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) films for ocular drug delivery: formulation, miscibility, in vitro and in vivo studies – Guzel K. Abilova, Daulet B. Kaldybekov, Elvira K. Ozhmukhametova, Aisulu Zh. Saimova, Diara S. Kazybayeva, Galiya S. Irmukhametova, Vitaliy V. Khutoryanski. ScienceDirect 2019

