Design and Development of Dual Functional Colon Targeted Eudragit/Chitosan Nanoparticles: A QbD Approach
Aim: The goal of this study was to develop colon-targeted nanoparticulate systems of the anti-inflammatory agent Quercetin (QU) and evaluate the formulation for various parameters that would allow the active ingredient to be released at a predetermined time and location with better pharmaceutical and therapeutic properties.
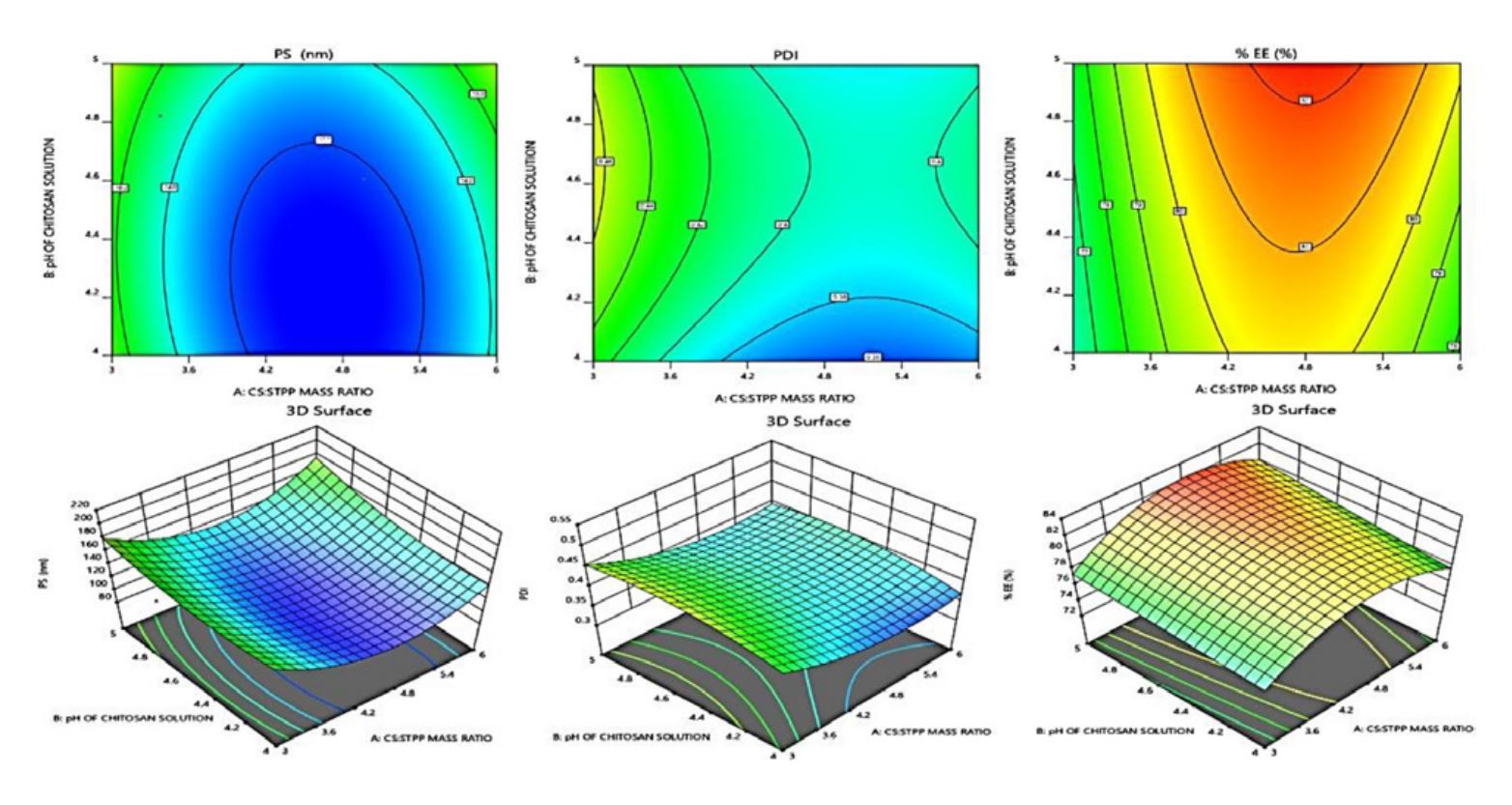
Materials and Methods: Quercetin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles were formulated for this purpose using the ionic gelation method by employing Central Composite Design. To coat Eudragit S 100 (ES 100) on an optimised formulation of quercetin loaded chitosan nanoparticles (QLCN), the oil in oil solvent evaporation process was used. Particle size (PS), polydispersity index (PDI), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and drug release (% DR) were evaluated to characterize the nanoparticles.
Results: Quercetin loaded chitosan nanoparticles has an average PS 114.2 ± 1.42 nm and polydispersity index 0.396 ± 0.02, whereas Eudragit coated nanoparticles shows PS 330.2± 0.40 nm and polydispersity index 0.412 ± 0.02. Surface morphology of prepared nanoparticles were confirmed using SEM. According to an in vitro drug release analysis of nanostructured formulations, the ES 100 coating on QLCN inhibits the release of quercetin in the upper gastrointestinal system, demonstrating good colon drug targeting.
Conclusion: According to an in vitro release study of nanoparticle formulations, the ES 100 coating on QLCN limits the release of quercetin in the upper gastrointestinal system, demonstrating effective colon drug targeting.
Download the full article as PDF here Design and Development of Dual Functional Colon Targeted Eudragit_Chitosan Nanoparticles_A QbD Approach
or read it here
Source: Priyadarshini Patel, Tejas Patel, Published on: September 2022, Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, 2022; 56(4):1063-1075, Original Article | doi:10.5530/ijper.56.4.187

