Improving the Powder Properties of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (Ethenzamide) with a Silica Nanoparticle Coating for Direct Compaction into Tablets
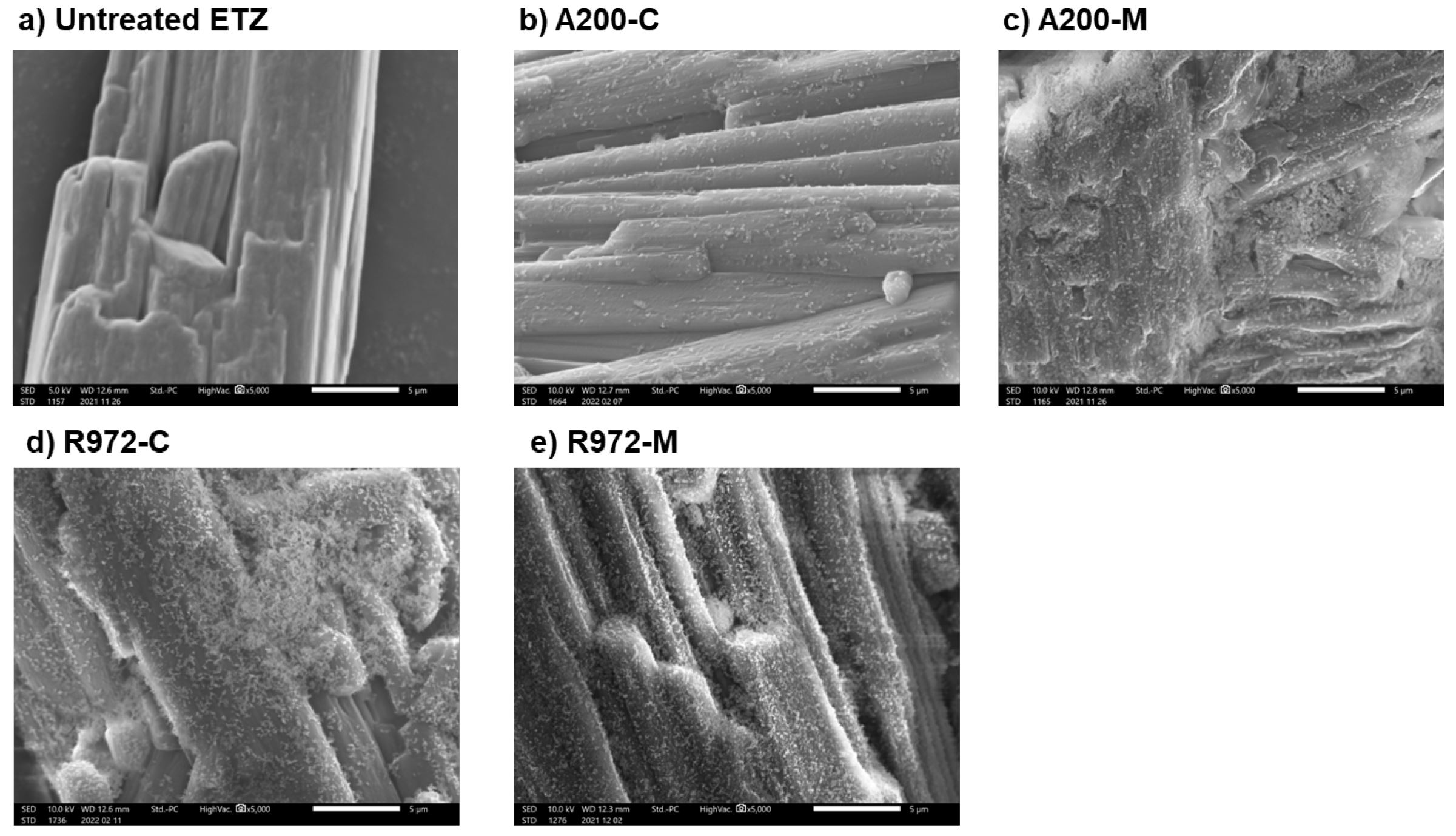
To improve the powder properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), we coated APIs with silica nanoparticles using a dry process that allowed for direct compression into tablets. The dry coating performed with different apparatuses (a batch-type high-speed shear mixer (Mechanomill) and a continuous conical screen mill (Comil)) and properties of the resulting dry-coated APIs were compared. Ethenzamide (ETZ), which has low powder flowability, was selected as the host particle to be improved and the colloidal silicas Aerosil 200 and R972 were used as the guest particles. Both coating processes and types of silica nanoparticles improved the powder flowability (angle of repose) of ETZ under unstressed conditions. Inverse gas chromatography demonstrated that dry coating with silica nanoparticles reduced the surface free energy and improved the homogeneity of the surface energy distribution of ETZ particles. Under the stress conditions of a shear cell test, the Mechnomill-based treatment improved the powder flowability of ETZ from that of untreated ETZ; however, the Comil-based treatment did not improve the flowability. The mechanical shear force exerted by Comil was apparently insufficient for interactions between host and guest particles. However, the properties of tableted ETZ were enhanced even when the silica nanoparticles were coated using Comil.
Download the full article as PDF here Improving the Powder Properties of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (Ethenzamide) with a Silica Nanoparticle Coating for Direct Compaction into Tablets
or read it here
Materials
ETZ was purchased from Iwaki Seiyaku (Tokyo, Japan). A200 and R972 were provided by Nippon Aerosil (Tokyo, Japan). Pharmatose 100M (lactose monohydrate) was provided by DFE Pharma (Nörten-Hardenberf, Germany). Ceolus PH 101 (microcrystalline Powders 2022, 1 233 cellulose) was provided by Asahi Kasei Corporation (Tokyo, Japan). Magnesium stearate was obtained from Kishida Chemical Co., Ltd. (Osaka, Japan).
Tadauchi, T.; Yamada, D.; Koide, Y.; Yamada, M.; Shimada, Y.; Yamazoe, E.; Ito, T.; Tahara, K. Improving the Powder Properties of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (Ethenzamide) with a Silica Nanoparticle Coating for Direct Compaction into Tablets. Powders 2022, 1, 231-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders1040016

