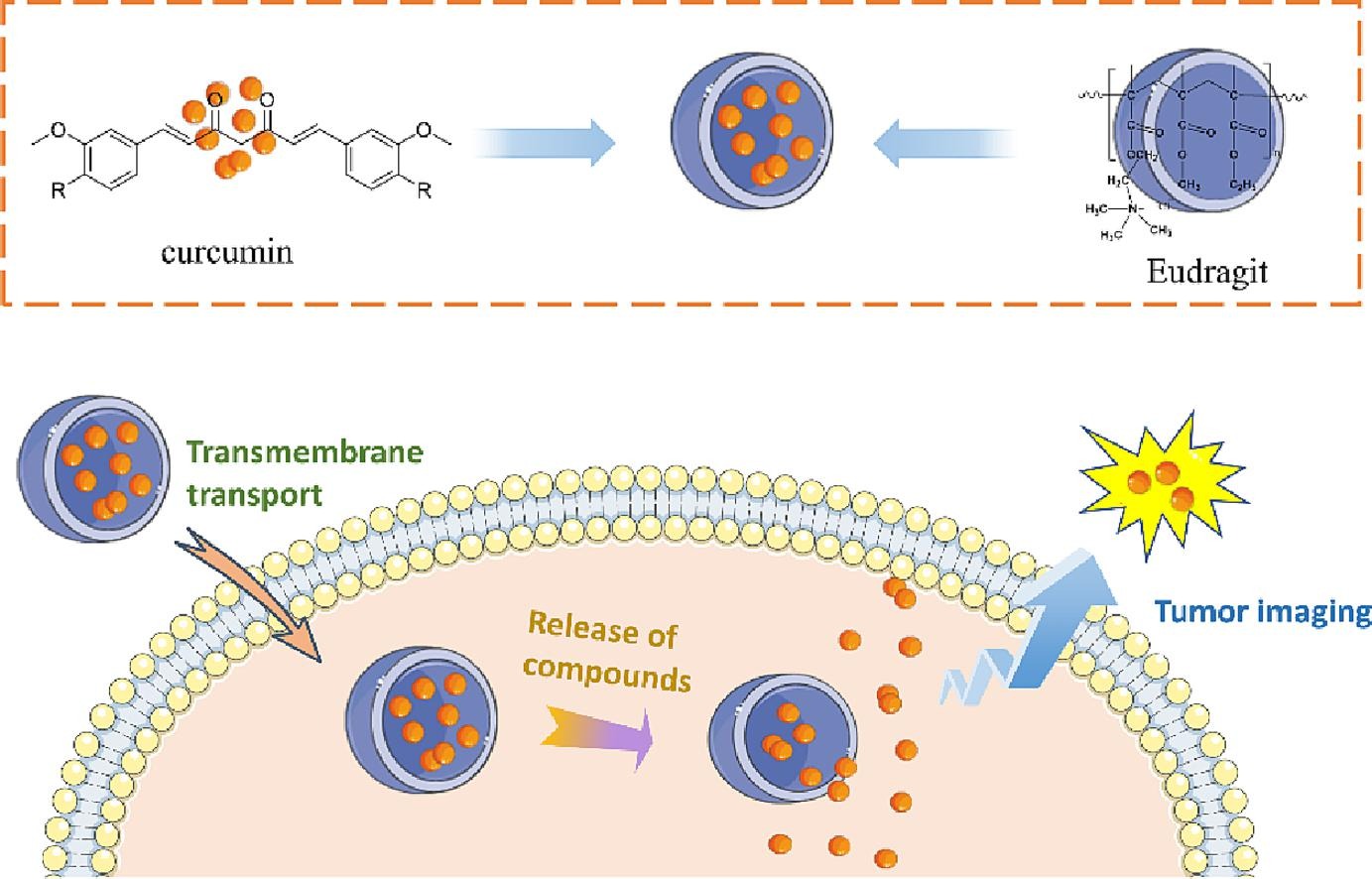
Strategy of eudragit coated curcumin nanoparticles delivery system: Release and cell imaging studies in simulated gastrointestinal microenvironments
Abstract
Curcumin has a broad-spectrum anti-tumor effect and has no toxic side effects. However, the unique diketone structure of curcumin will undergo diketo-enol tautomerism under different acid-base conditions, resulting in its instability under physiological conditions. In addition, the low biocompatibility and absorption rate of curcumin also limit the use of curcumin drugs. In this paper, curcumin was modified by substitution of acryloyl and acrylsulfonyl groups, and four kinds of nanoparticles with regular morphology were prepared using non-toxic and non-irritating acrylic resin as coating material to improve the stability and bioavailability of the compounds. Zeta potential testing shows that the composites surface carries positive charges and have good stability. In the release experiment, four complexes have the potential for slow and controlled release. Imaging of Hela cells with different channels was performed, and the imaging results showed that the complexes could enter the cells and be absorbed by them, demonstrating good imaging performance. MTT experiments have shown that the complexes have certain anti-tumor activity and low cytotoxicity. In general, the complexes synthesized in this paper have potential in the field of drug fluorescence imaging detection. At the same time, this experiment provides a new idea for the design of slow and controlled release of drugs.
Introduction
Currently, malignant tumors are a threat to human health. Common treatments for malignant tumors include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, but these treatments have limitations such as poor prognosis and high recurrence rates. Therefore, there is a need to find a solution that is superior to conventional oncology treatments. Curcumin is a natural polyphenolic compound extracted from the genus curcuma. It has broad-spectrum anti-tumor effect [1]. Curcumin can inhibit the abnormal proliferation, local infiltration, metastasis and invasion of tumor cells by regulating the division cycle of tumor cells to achieve anti-tumor effects [2]. In addition, curcumin has pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammation [3], anti-infection, anti-oxidative stress [4] and antibacterial [5]. However, curcumin, a hydrophobic molecule [6], does not penetrate cell membranes and does not reach effective therapeutic concentrations in blood and cells [7], resulting in poor bioavailability [8]. Besides, curcumin is structurally unstable in the physiological environment of the body and curcumin metabolizes and excretes fast from the body [9], limiting its development in the field of medicine. Therefore, structural modification [10] of curcumin is needed to obtain more stable, better water-soluble and more active compounds [11], [12]. The development of new dosage forms [13] and technologies [14], [15], [16], [17] (solid dispersion [18], emulsions, liposomes [19], polymeric micelles, clathrate compound [20]) also make it possible to improve the water solubility of curcumin.
Drug inclusion technology is to embed the drug to the carrier, and use the physical and chemical properties of the carrier to solve the problems of low solubility and poor stability of the drug in the delivery process, so as to improve the bioavailability. Eudragit has been widely used in the field of pharmaceutical coating delivery due to its stability, good biocompatibility, non-toxic and non-irritating properties and its smooth and compact coating film [21], [22]. The Eudragit RL100, RS100 series are formed by replacing ethyl acrylate and methyl methacrylate monomers with different amounts of chlorotrimethylamino ethyl methacrylate to form a copolymer skeleton [23]. Eudragit RL100 and RS100 are insoluble in water, but due to their presence of quaternary amine groups, nano formulations have certain swelling and permeability, allowing water to slowly penetrate [24]. Therefore, they can regulate the release behavior of drugs to achieve optimal therapeutic effects and improve bioavailability. Eudragit RL100 and RS100 are widely used in the continuous delivery research of drugs such as nebivolol [25] and diclofenac [26]. Eudragit, as a safe and non-toxic polymer material, is easy to be absorbed by oral administration. As a carrier of curcumin drugs, Eudragit is expected to improve the stability of drugs and deliver the drug to the action site to improve the utilization rate. At the same time, it can control drug release through specific combination with curcumin, extend the drug action time, improve the bioavailability, and reduce the toxic and side effects of anticancer drugs.
In this work, acrylic resin is used to coat curcumin compounds to improve the solubility, stability and biocompatibility of the drug. After several simple reactions, a series of curcumin derivatives coated with acrylic resin were obtained. In order to observe its optical properties and stability, the compounds were tested. At the same time, releasing test in vitro, cell imaging experiments and cytotoxicity assays were carried out to observe the biocompatibility of the polymers. This study aims to improve the solubility and stability of curcumin derivatives, and provide reference for the development and application of sustained and controlled release drugs.
Read more here
Ying Liu, Meng Zhou, Shuo Wang, Jiankang Feng, Chichong Lu, Guofan Jin, Strategy of eudragit coated curcumin nanoparticles delivery system: Release and cell imaging studies in simulated gastrointestinal microenvironments,
Bioorganic Chemistry, Volume 139, 2023, 106732, ISSN 0045-2068, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106732
Read more articles about “Bioavailability Enhancement” here: