Evaluation of the effect of polymer composition on the rheological, mechanical properties and drug released behavior of novel Eudragit L100-55/ gelatin gastro-resistance uncoated capsule
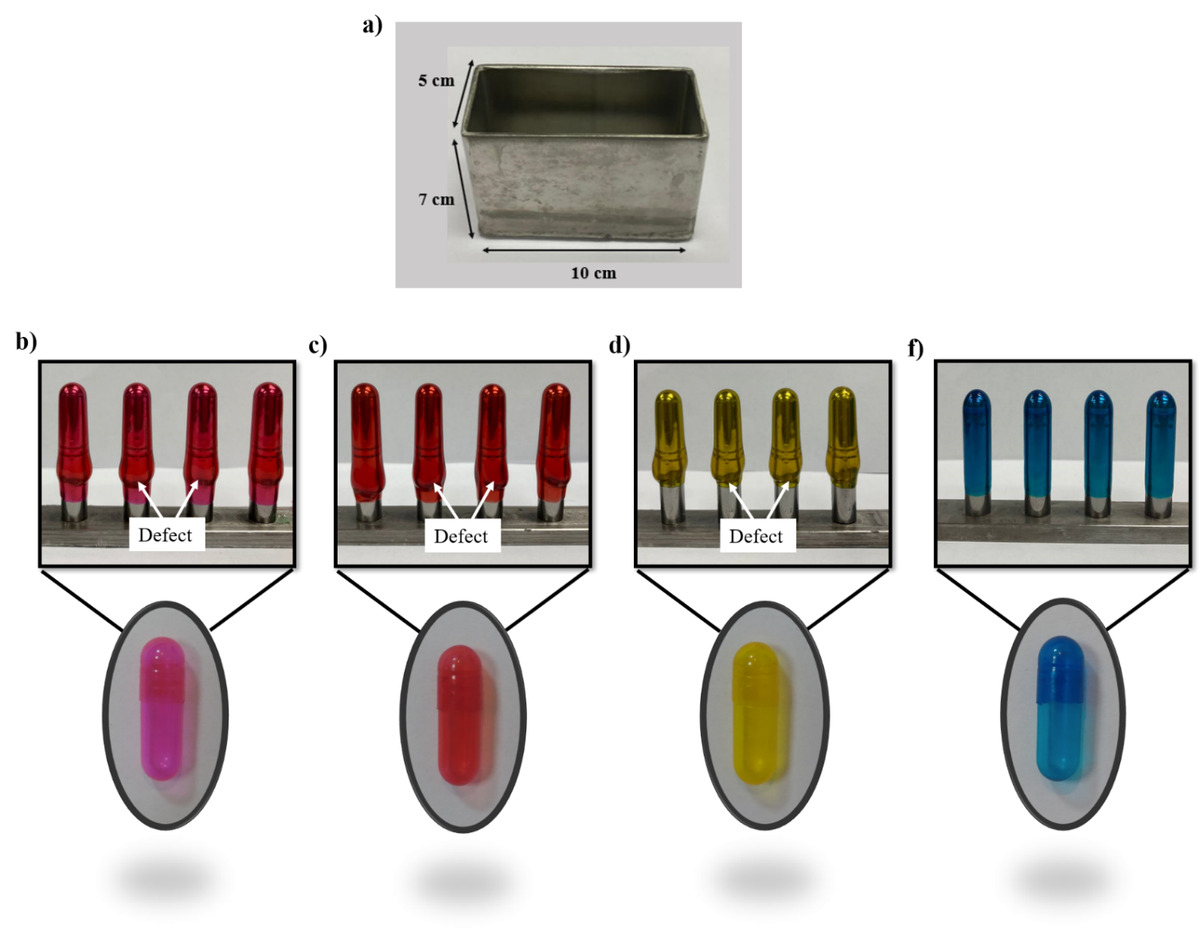
Capsules have been investigated as a popular oral dosage form among communities due to their simplicity and ease of production. Capsules that are considered in the gastro-resistance category can be very beneficial due to enhanced drug absorption, improved stability, targeted release, etc. This study investigated the effect of enteric polymers on uncoated hard capsule fabrication and dissolution properties. The polymers used in this study included HPMCPh and Eudragit L100-55. Eight different formulations based on HPMCPh, Eudragit, and gelatin were examined to identify the ideal formulation for the product of uncoated enteric hard capsules with preferred physicochemical and gastro-resistance properties. The results reveal that the capsules containing Eudragit (F1), HPMCPh (F2), Eudragit/HPMCPh/gelatin (F3), and Eudragit/gelatin (F4) are steady within the simulated stomach environment, and drug release does not occur for 120 minutes. The outcomes demonstrate that, among the proposed formulas, the F4 formula is suitable both in terms of capsulation form and delayed release properties and shows no microbial growth. The properties of the optimized sample were studied by FTIR, FESEM, tensile strength, humidity, and rheology. The results illustrated that gelatin-based hydrogels with Eudragit (F4) are potential candidates for manufacturing uncoated enteric hard capsules that inhibit drug release in a gastric pH medium and act as a pH-sensitive drug release system.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw materials and chemicals
All raw materials used in this work were utilized in an as-received form without any additional process and purification. Gelatin type B was acquired from Rousselot (France), (HPMCPh) (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate) and Eudragit L100-55 (poly (methacrylic acid-co-ethyl acrylate) (1:1)) were provided in-kind as samples from LOTTE Fine Chemical (South Korea) and Rahavard Tamin pharmaceutical co., respectively. Polyethylene Glycol 400 (PEG-400; H(OCH2CH2)nOH) was used as a plasticizer, Trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4.12H2O), tryptic soy broth (TSB) and Hydrochloric acid 35% (HCl), were acquired from Merck. Aqueous solution of ammonia (NH3, 1N) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 0.2N) were used as the solvents for HPMCPh and Eudragit. Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS; NaC12H25SO4) was purchased from Godrej Industry (India). Colloidal Nano silicon dioxide (SiO2) was obtained from Evonik (Germany), Propylene glycol (PG) and Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4.7H2O) were purchased from Kimyagaran Emrooz Chemical Industries Co.(Iran) and Behansar (Iran), respectively. Further additives, including Propylparaben (C10H12O3) and Methylparaben (C8H8O3) were provided by UENO Fine Chemical Industry (Japan). Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate (PSS; C16H17F2N3NaO5S) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The material for determination of microbial levels was tryptic soy agar (TSA), sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA), eosin methylene blue agar (EMB), rappaport-vassiliadis soya peptone (RVS), cystine tryptic agar (CTA), macConkey broth (MACB) and mannitol salt agar (MSA) that acquired from Merck.
Download the full article as PDF here: Evaluation of the effect of polymer composition on the rheological, mechanical properties and drug released behavior of novel Eudragit L100-55/ gelatin gastro-resistance uncoated capsule – Preprint (not peer reviewd)
or read it here
Ramin Ramezani Kalmer, Afzal Karimi, Samira Gholizadeh Dogaheh et al. Evaluation of the effect of polymer composition on the rheological, mechanical properties and drug released behavior of novel Eudragit L100-55/ gelatin gastro-resistance uncoated capsule, 01 March 2024, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square
https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3995664/v1

