Intranasal Insulin Delivery: Microparticle Formulations Consisting of Aloe vera Polysaccharides for Advanced Delivery across Excised Olfactory and Respiratory Nasal Epithelial Tissues
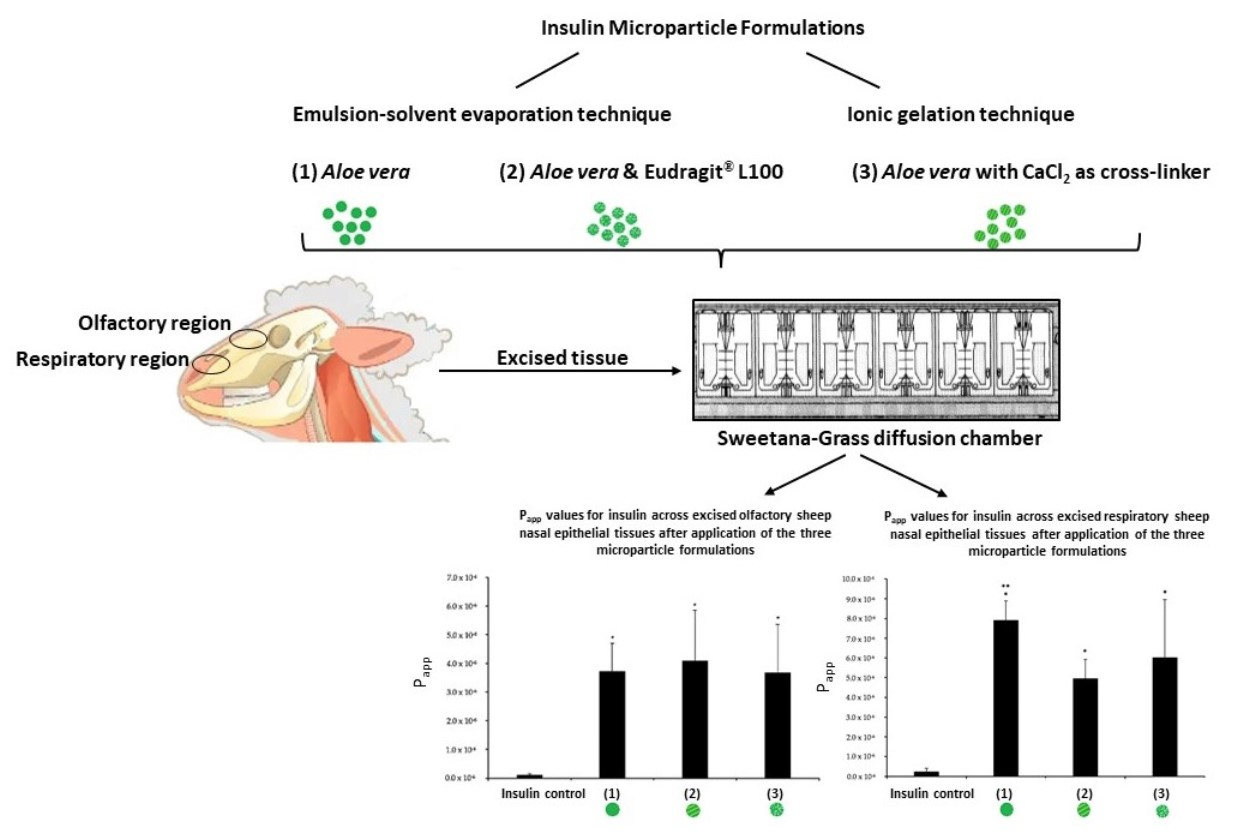
Aloe vera gel and whole leaf materials, as well as polysaccharides, precipitated from the gel, have previously been shown to enhance macromolecular drug delivery across epithelial tissues. This study investigated the effectiveness of microparticle formulations prepared from A. vera polysaccharides for nasal delivery of insulin across excised sheep olfactory and respiratory nasal epithelial tissues. An emulsion-solvent evaporation technique was used to prepare two insulin microparticle formulations, namely one containing Eudragit® L100 and A. vera polysaccharides and one containing A. vera polysaccharides only. In addition, an ionic gelation technique was used to prepare an insulin microparticle formulation with A. vera polysaccharides, where calcium chloride was used as a cross-linker. The microparticle formulations were evaluated in terms of drug content (assay), particle size, drug release (dissolution), ex vivo drug permeation, and histology. The microparticle formulations exhibited statistically significantly higher insulin delivery across excised sheep olfactory and respiratory nasal epithelial tissues compared to that of the control group (insulin alone). In conclusion, the use of A. vera polysaccharides in microparticle formulations significantly improved nasal insulin delivery. Therefore, A. vera polysaccharide containing microparticles showed high potential to enhance systemic bioavailability and delivery into the brain of macromolecular drugs such as insulin after intranasal administration.
2.1. Materials
Download the full study as PDF here: Intranasal Insulin Delivery: Microparticle Formulations Consisting of Aloe vera Polysaccharides for Advanced Delivery across Excised Olfactory and Respiratory Nasal Epithelial Tissues
or read it here
Kirby-Smith, C.; Steenekamp, J.; Steyn, D.; Haasbroek-Pheiffer, A.; Hamman, H.; Hamman, J. Intranasal Insulin Delivery: Microparticle Formulations Consisting of Aloe vera Polysaccharides for Advanced Delivery across Excised Olfactory and Respiratory Nasal Epithelial Tissues. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084822

