Oral insulin delivery: Barriers, strategies, and formulation approaches: A comprehensive review
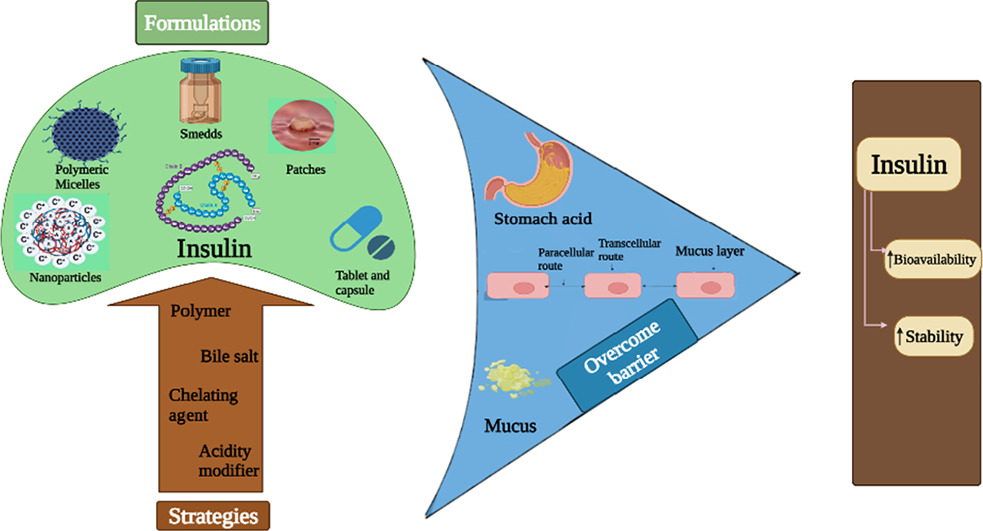
Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by a hyperglycemic condition which can either be caused by the destruction of the beta cells or by the resistance developed against insulin in the cells. Insulin is a peptide hormone that regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus needs the use of Insulin for efficient management. However invasive methods of administration may lead to reduced adherence by the patients. Hence there is a need for a non-invasive method of administration. Oral Insulin has several merits over the conventional method including patient compliance, and reduced cost, and it also mimics endogenous insulin and hence reaches the liver by the portal vein at a higher concentration and thereby showing improved efficiency.
Highlights
- Barriers to oral insulin delivery along with suitable approaches reviewed comprehensively.
- Description of the formulations explored for insulin and other proteins/peptides for oral delivery.
- Ingenious approaches for oral delivery like self-orientation system and stimuli-based release, presented.
- Clinical trials and Patents on oral insulin giving insight into the current scenario and future trends discussed.
However oral Insulin must pass through several barriers in the gastrointestinal tract. Some strategies that could be utilized to bypass these barriers include the use of permeation enhancers, absorption enhancers, use of suitable polymers, use of suitable carriers, and other agents. Several formulation types have been explored for the oral delivery of Insulin like hydrogels, capsules, tablets, and patches which have been described briefly by the article. A lot of attempts have been made for developing oral insulin delivery however none of them have been commercialized due to numerous shortcomings. Currently, there are several formulations from the companies that are still in the clinical phase, the success or failure of some is yet to be seen in the future.
Read more
S. Spoorthi Shetty, Praveen Halagali, Asha P. Johnson, K.M. Asha Spandana, H.V. Gangadharappa, Oral insulin delivery: Barriers, strategies, and formulation approaches: A comprehensive review, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Volume 242, Part 3, 2023, 125114, ISSN 0141-8130,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125114.
See our next webinar:
(click the picture for free registration)


