Optimization of radial extrusion and pellet coating processes using pat approaches
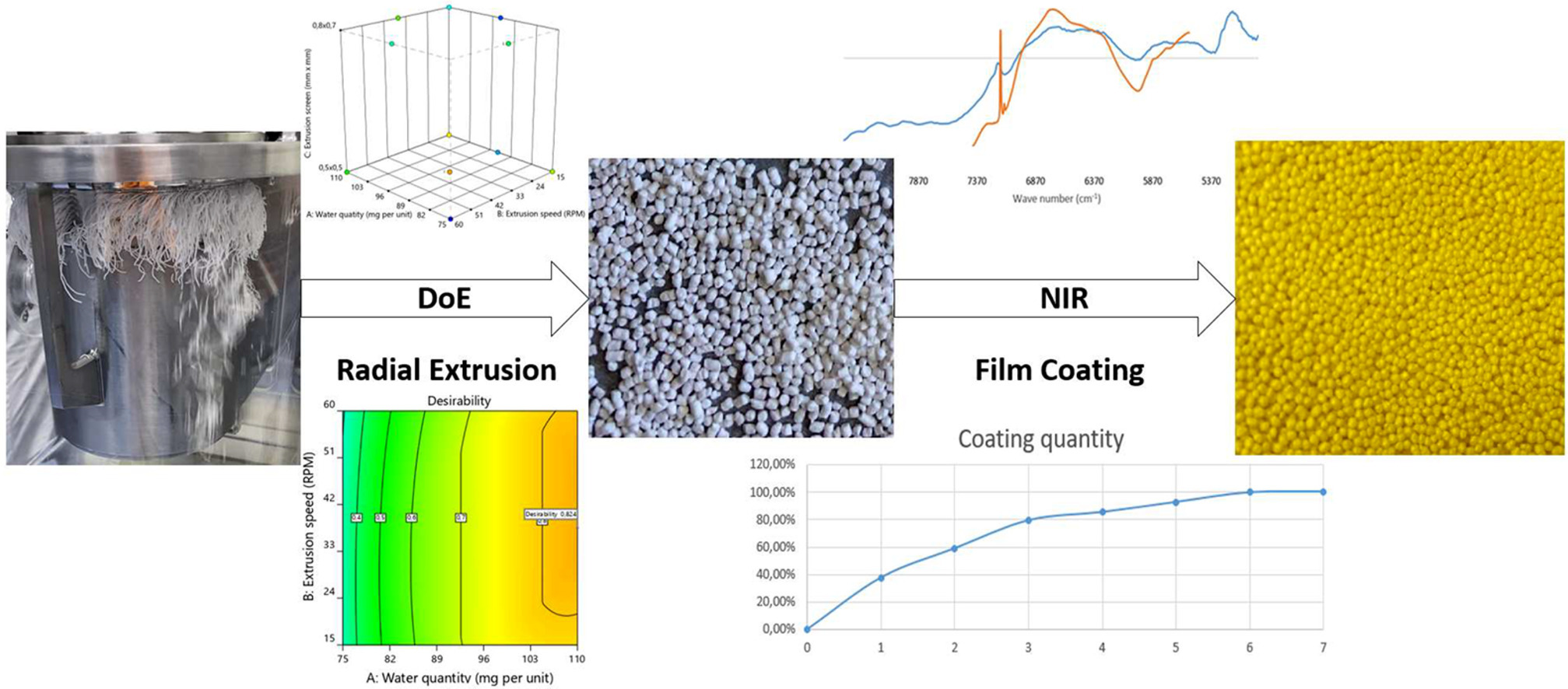
FDA’s initiative Pharmaceutical CGMPs for the 21st century opened the door for introduction of several risk based approaches in pharmaceutical industry. One significant advancement that has emerged is the implementation of process analytical technology (PAT), which has opened doors for understanding and controlling complex technological processes. Two such processes, radial extrusion and pellet coating, offer a solid foundation for the application of PAT tools due to their numerous critical process parameters. The aim of the first part of the study was to optimize the neutral pellet production to produce the pellets with properties desired for successful film coating using design of experiments (DoE). In the second part the optimized pellets underwent film coating and the coating quantity was predicted in real or near real-time using in-line and at-line NIR probes and the performance of both probes was compared.
The desired properties of the pellets, narrow particle size distribution, high sphericity and high process yield, were successfully achieved. Models for film coating quantity prediction using in-line and at-line NIR probe were successfully calibrated and tested by coating two additional batches. Despite the limited sample size for model calibration, at-line NIR exhibited excellent prediction performance and enabled accurate determination of process end-point. The coating quantity determined by UV/VIS spectroscopy in both test batches deviated by less than 2.0% from the target value. However, the in-line NIR probe, primarily due to its inferior spectral resolution, displayed a slightly lower quality of the calibrated model and notable overprediction for the tested batches.
2. Materials
Neutral pellets were manufactured using microcrystalline cellulose type 102 (MCC; Vivapur® 102; JRS Pharma, Germany) with average particle size 130 µm and binder polyvinyl-pyrrolidone (PVP; Kollidon® K-30; BASF; Germany). Suspension for film coating of pellets was prepared using polymer hydroxypropylmethyl-cellulose type 2910 with viscosity 6 mPas (HPMC; Pharmacoat® 606; Shin-Etsu; Japan), talc (Imerys talc; Italy) and tartrazine sodium salt (Sigma Aldrich, USA) that was used as a model active pharmaceutical ingredient based on its suitability for quantity determination using UV-VIS spectroscopy. Purified water was used as a solvent in granulation liquid and film coating suspension.
Download the full Journal Pre-proof as PDF here: Optimization of radial extrusion and pellet coating processes using pat approaches – Journal Pre-proof
or read it here
A. Gradišek, G. Ratek, F. Vrečer, K. Korasa, OPTIMIZATION OF RADIAL EXTRUSION AND PELLET COATING PROCESSES USING PAT APPROACHES, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2023, 106595, ISSN 0928-0987,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106595.


