Accelerating Topical Drug Development Through Initial Excipient Selection

See the poster presented by Seppic at DDF Summit in Berlin in June 2023:
Introduction
Novel topical drug development will require multiple formulation adjustments from the initial formulation studies to the registration phase [1].
Common issues encountered are API chemical instability, API lack of solubility, dosage form instability, optimization of the skin delivery, mitigation of side-effects.
pH adjustment and change of nature or concentration of solvents, penetration enhancers and emollients can be relevant adjustments [2]. However, each adjustment is at risk of disrupting polymeric and surfactant systems, causing further delay in formulation and drug development [3].
There is a need for stabilizing excipients able to provide the same performance independently from formulation changes.
Material & Method
Thickening / Stabilizing Polymer
Acrylamide / Sodium Acryloyldimethyl Taurate Copolymer in inverse emulsion
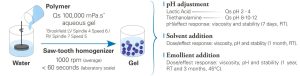
Stability to formulation adjustments
Impact of pH adjustment on the polymer network
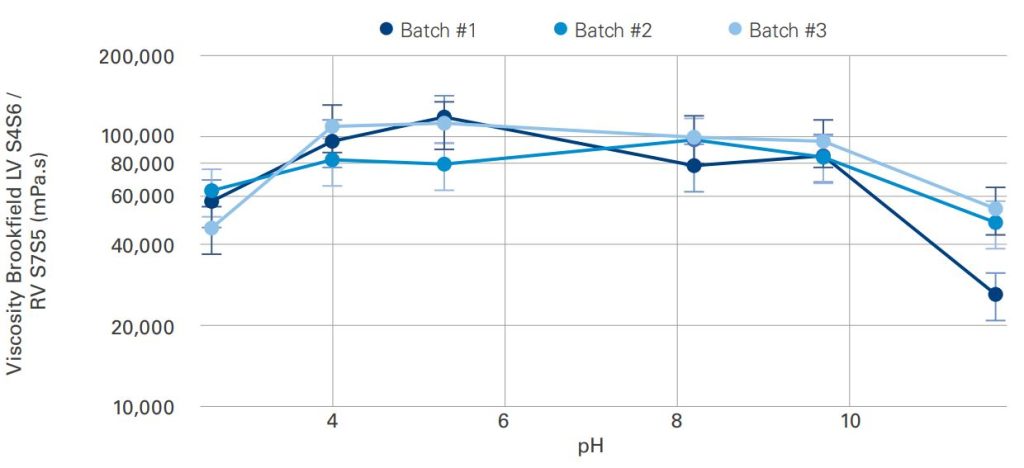
From pH 4 to 10, the gels obtained have comparable viscosities with no impact even with pH adjustment.
The Acrylamide / Sodium Acryloyldimethyl Taurate Copolymer shows a good batch-to-batch reproducibility.
Extreme acid or basic pH tend to decrease the gels viscosity. An increase of polymer concentration can compensate for this viscosity loss.
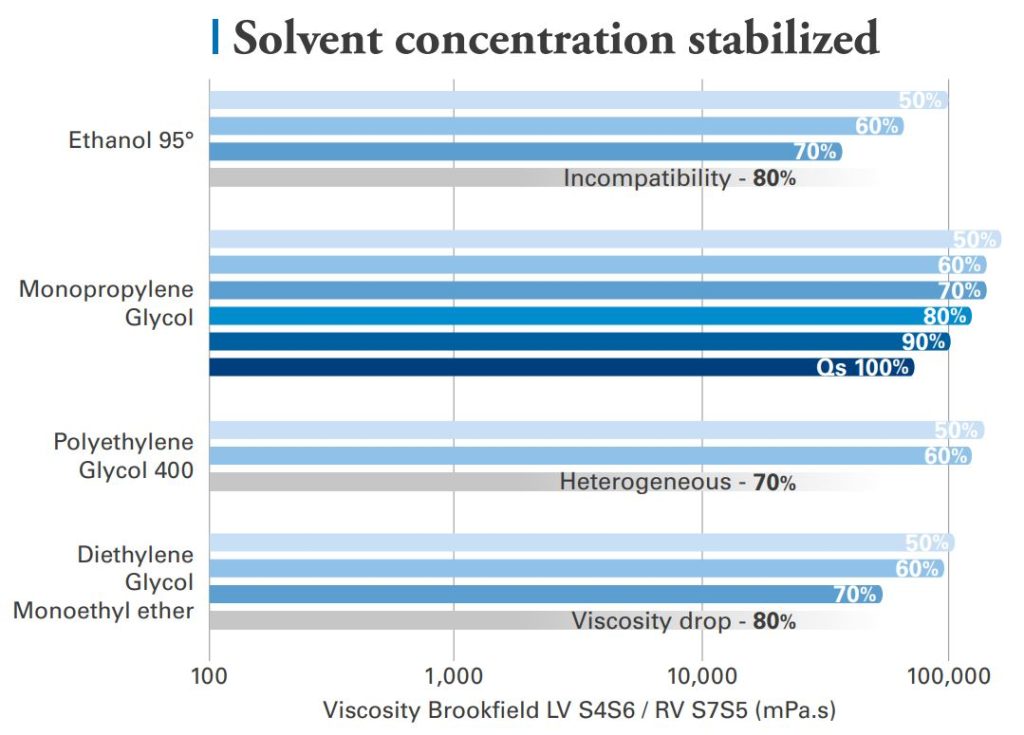
The gels of Acrylamide / Sodium Acryloyldimethyl Taurate Copolymer can stabilize at least 60% of tested solvents with close resulting viscosities.
At higher solvent concentration, Ethanol shows the most viscosity impact, while PEG-400 from 70% concentration causes phase segregation.
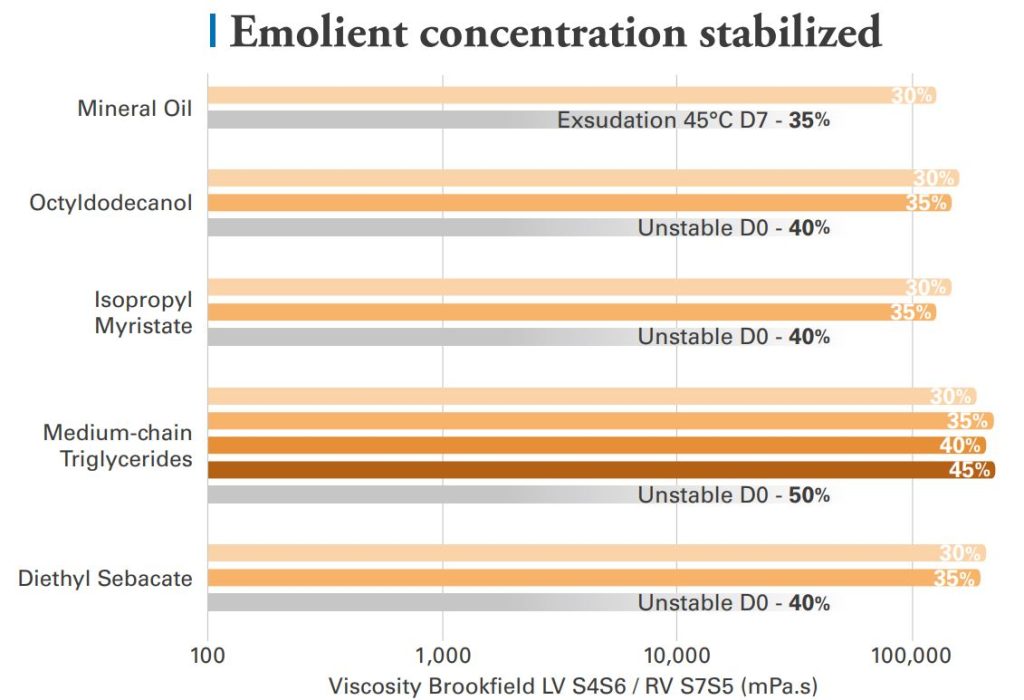
Acrylamide / Sodium Acryloyldimethyl Taurate Copolymer gels can stabilize at least 30% of tested emollient with comparable resulting viscosities.
Change of oil nature have limited impact on the dosage form stability, though higher emollient concentrations can be reached with medium-chain triglycerides.
Authors: Benjamin GAVINET, Benoît SOUYRI, Emilie TONGLET, Maïté CAVAILLÈS, Alice DANESHVAR
See the full poster on “Accelerating Topical Drug Development Through Initial Excipient Selection” here
(click the picture to download the poster)
Source: Seppic poster “Accelerating Topical Drug Development Through Initial Excipient Selection”
Do you need more information or a sample of excipients by Seppic?


