Advancement in Solubilization Approaches: A Step towards Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drugs
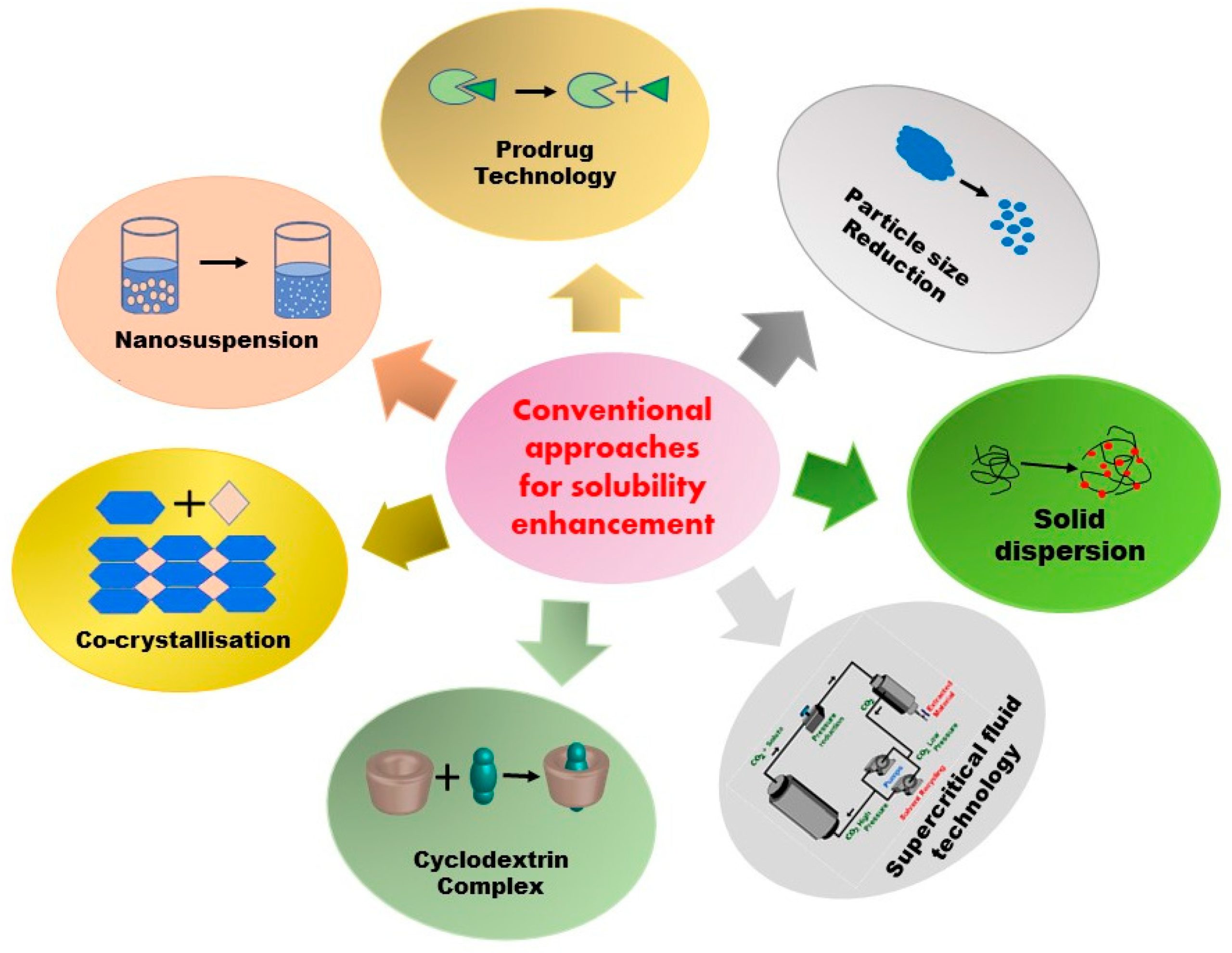
A drug’s aqueous solubility is defined as the ability to dissolve in a particular solvent, and it is currently a major hurdle in bringing new drug molecules to the market. According to some estimates, up to 40% of commercialized products and 70–90% of drug candidates in the development stage are poorly soluble, which results in low bioavailability, diminished therapeutic effects, and dosage escalation. Because of this, solubility must be taken into consideration when developing and fabricating pharmaceutical products. To date, a number of approaches have been investigated to address the problem of poor solubility. This review article attempts to summarize several conventional methods utilized to increase the solubility of poorly soluble drugs.
Highlights
These methods include the principles of physical and chemical approaches such as particle size reduction, solid dispersion, supercritical fluid technology, cryogenic technology, inclusion complex formation techniques, and floating granules. It includes structural modification (i.e., prodrug, salt formation, co-crystallization, use of co-solvents, hydrotrophy, polymorphs, amorphous solid dispersions, and pH variation). Various nanotechnological approaches such as liposomes, nanoparticles, dendrimers, micelles, metal organic frameworks, nanogels, nanoemulsions, nanosuspension, carbon nanotubes, and so forth have also been widely investigated for solubility enhancement. All these approaches have brought forward the enhancement of the bioavailability of orally administered drugs by improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. However, the solubility issues have not been completely resolved, owing to several challenges associated with current approaches, such as reproducibility in large scale production. Considering that there is no universal approach for solving solubility issues, more research is needed to simplify the existing technologies, which could increase the number of commercially available products employing these techniques.
Excipients mentioned in the study besides others: Cyclodextrins, Povidones (PVP), polyethylene glycols (PEGs), hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), and Plasdone-S 630. Surfactants such as sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS), docusate sodium, Pluronic-F68, Myrj-52, and Tween-80
Download the full article as PDF here: Advancement in Solubilization Approaches: A Step towards Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drugs
or read it here
Kumari, L.; Choudhari, Y.; Patel, P.; Gupta, G.D.; Singh, D.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Bansal, K.K.; Kurmi, B.D. Advancement in Solubilization Approaches: A Step towards Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Life 2023, 13, 1099.
https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051099

