Lipid Excipients for Cannabinoid Drug Products

With an enhanced understanding of the medicinal benefits and looming ease of regulations around
the globe, there is an expressed need for science based, adequately dosed, and age appropriate
cannabinoid medicines.
The benefits of medicinal cannabinoids include:
✓ Controlled and measured dosing
✓ Age appropriate, patient-centric dosage forms
✓ Alternatives to unhealthy modes of intake such as vaping or smoking
Properties of Cannabinoids
Among the hundreds of phytocannabinoids and terpenes isolated from cannabis, two very lipophilic
molecules stand out: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Amounting between 30%
and 50% of a single plant’s weight, they are known to affect physiological processes such as mood,
memory, appetite, and pain sensation. They function by activating the endocannabinoid receptors of
the nervous system which are found throughout the body, including in the brain.
THC and CBD have been extensively studied and are found to have unique qualities of their own
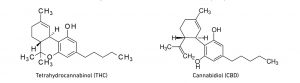
THC is responsible for the euphoric and psychoactive effects of cannabis and has applications as medicine
for treatment of chronic pain and nausea associated with chemotherapy. Another indication for THC is the
treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), i.e. potential delay in the progression of the disease and
alleviation of the ALS symptoms. CBD on the other hand is a non-psychoactive, anti-inflammatory medicine.
It is preferred over THC by patients in need of treatment for arthritis, mood disorders, and nausea.
Studies have shown that THC and CBD have oral bioavailability of approximately 3% to 8% and this
varies by formulation and type of vehicles used. This poor bioavailability is in part attributed to the poor
gastrointestinal (GI) solubility of these compounds resulting in erratic and variable absorption from the
GI tract. Additionally, a significant first pass metabolism may ensue in the liver following GI absorption.
These properties render cannabinoids as excellent candidates for Lipid-Based Drug Delivery (LBDD).
The Benefits of Lipid Excipients in Oral Drug Delivery
Lipid formulations are shown to improve the bioavailability of cannabinoids by improving solubility,
intestinal permeability, and enhancement of the lymphatic route of absorption. Among the key
mechanisms associated with oral lipid formulations in enhancing bioavailability is the improved drug
wettability and dispersion in the GI fluids, through natural digestion mechanisms that help maintain
drug solubilization in vivo. The effect lasts long enough for the drug to approach the enterocytes
for absorption. Recent studies have found that the bioavailability of THC and CBD from a sesame oil
formulation was 2.5-fold and 2.9-fold higher compared to a lipid-free formulation.
However, not all lipids are equal in the nature of their impact on permeability and absorption. Lipid
systems may vary by fatty acid chain length and the type/degree of esterification. The choice of
excipient is guided by the overall objectives of the dose and the type of dosage form e.g. tablet, capsule,
or powder. The formulation may be fine-tuned to improve lymphatic absorption and/or rate of drug
release.
Due to their unique properties and versatility, lipid formulations may be designed to tackle several of
the below listed bioavailability objectives in a single lipid formulation:
✓ Solubilization of the API in the dose
✓ Drug dispersion and dissolution in the GI tract
✓ Enhanced permeability across enterocytes and wider absorption window
✓ Enhanced lymphatic transport of lipophilic drugs
LIPIDS EXCIPIENTS FOR CANNABINOID DRUGS
Excipients for Oral Delivery
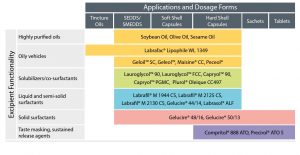
Gattefossé offers a range of excipients for achieving one or more of the objectives listed above.
They may be categorized by physical state (liquid vs. solid), melting point, HLB value, as well as
biopharmaceutical aspects.
As summarized in Table 2, products like Maisine® CC, Peceol®, Labrafil® M 1944 CS, Labrafil® M 2125
CS and the Highly Purified Oils are suitable for oily formulations which may be filled into capsules.
They may also be used as oil phase in self-emulsifying formulations. Long chain fatty acids (LCFA)
constitute the bulk of the fatty acids found in the products listed, exceptions being Labrafac® series,
Lauroglycol™ series, Capryol™ series, and Labrasol® which are composed of medium chain fatty
acids (MCFA) with carbon chain lengths of C8 and C10.
Lymphatic vs. Hepatic Absorption
The fatty acid chain length plays a key role in the emulsification, permeation, and route of absorption.
The medium chain esters are known for rapid, hepatic absorption, whereas products consisting of
unsaturated LCFA tend to stimulate chylomicron secretion and increase lymphatic uptake. The process
can enhance the bioavailability of highly lipophilic drugs through preferential absorption within the
lymphatic transport system, consequently decreasing first-pass metabolism of the drug in the liver.
Since absorption by the lymph means bypassing the liver, formulation with unsaturated LCFA can
be a promising strategy for cannabinoids, which are metabolized extensively in the liver. Moreover,
lipid excipients may be selected for their surfactive and often self-emulsification properties. Selfemulsification refers to the unique property of certain lipids that disperse spontaneously in aqueous
media, forming micellar and lamellar self-assemblies, which are key in maintaining solubility and
improving permeability of poorly soluble drugs such as cannabinoids.
See more on Lipid Excipients for Cannabinoid Drugs
SEDDS/SMEDDS
With careful selection of the excipients having the right fatty acid chain length, melting point, and
emulsification properties, it is possible to design sophisticated dosage forms. As an example, self
(micro) emulsifying drug delivery systems known as SEDDS and SMEDDS are a suitable solution to
improving oral drug delivery of poorly soluble and low permeability drugs.
Labrasol®, Gelucire® 44/14, Gelucire® 48/16, Gelucire® 50/13 and the Labrafil® series (Table 2) consist
of self-emulsifying excipients that may be in SEDDS / SMEDDS. Several of these products listed are
liquid or semi-solid, hence suitable for soft or hard shell capsules.
Other products, such as Gelucire® 48/16 and Gelucire® 50/13 are solids (higher melting points) and so are suitable also for preparation of granules and powders which can subsequently be filled into hard shell capsules or sachets. Alternatively, the powders may be compressed into tablets.
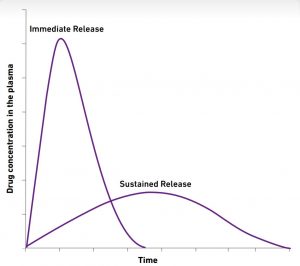
Generally, self-emulsifying formulations provide a rapid (immediate release) profile. Compritol® 888 ATO and Precirol® ATO 5 on the other hand are applicable to taste masking and the preparation of sustained release delivery systems in the form of granules or tablets.
Formulation Guidelines
Further practical information regarding formulation considerations for lipid formulations can be found in
our Formulation Guidelines: Developing Lipid Based Formulations for Oral Bioavailability Enhancement.
Additionally, it is possible to develop unique combinations of excipients to simultaneously achieve
enhanced bioavailability and sustained delivery. Additional information on sustained release development
is available in our Sustained Release Formulation Guidelines.
Meet Gattefossé at CPhI at STAND 102B80
The Benefits of Lipid Excipients in Dermal Drug Delivery
Skin as Route of Administration
With an average thickness of 1.2 mm and an acidic pH ranging from 4.2 to 6.1, the skin makes up
roughly 15% of the total weight of an adult. Certain therapies may target the skin, or a local area
beneath the skin. Others target the systemic circulation, often for a sustained delivery. Therefore,
good knowledge of the skin’s physiology and the proper role of excipients is essential in formulating
effective topical treatments.
Dosage Forms
In certain cases, cannabinoids need to be applied locally on the skin for various purposes such as
anti-acne, anti-psoriatic, anti-fungal, analgesics and anti-inflammatory applications. These may be in
topical dosage forms having various sensorial properties / textures, and a range of viscosities.
Other possibilities include ointments, foams, and gels. The choice of dosage form will largely depend on the intended use conditions such as spreadability over a given surface area of the skin, frequency of use, and the intended cannabinoid concentration to be delivered. Additionally, enhancers may be added to improve the rate of drug penetration and permeation into the dermis. Another important consideration is whether the formulation is to remedy a brief episode or a lingering ailment. Proven safety and absence of irritation potential become essential for chronic treatments.
Excipients for Topical Formulations
An overview of Gattefossé emulsifiers, consistency agents, and solubilizers suitable for topical
preparations is provided in Figure 3. With excellent tolerance / safety profiles and long history of use,
these are products of choice for developing stable and luxurious textures.
Each product listed below has unique advantages. Emulsifying bases are ready-to-use formulation
systems designed to simplify and to drastically reduce cost/time for development and production;
Tefose® 63 is a very mild base with precedence of use in vaginal preparations for many decades;
Gelot™ 64 can help emulsify high levels of polar oils; Labrasol® and Labrafil® are permeation enhancing emulsifiers that can be incorporated in all formulations. Likewise, Transcutol® P, a hydroalcoholic solubilizer and enhancer is suitable for a wide range of dosage forms. Microemulsions on the other hand are unique in their transparency, low viscosity and superior permeation enhancing capacity.

Penetration and Permeation Enhancers – Transcutol® P
A number of excipients such as the Labrasol® and Labrafil® series, Plurol® Oleique CC 497,
Lauroglycol™ series, Capryol™ series, and Transcutol® P are solubilizers as well as skin penetration
and permeation enhancers. They are often used in combination to modulate drug delivery to/or
across the skin.
Transcutol® P is globally known to solubilize and enhance the penetration of many drugs, notably
THC and delivery across skin layers. Using quantitative autoradiography methods, an independent
study (Fabin, 1991) measured the penetration of THC in rat skin from three different enhancing
formulations: neat Transcutol® P, PEG 400, and a 7:3 blend of propylene glycol/ethanol. The neat
Transcutol® P formulation showed the highest and the most stable THC distribution profile across
the skin layers. The results for 24 hours of application (Figure 3) show that the THC concentration
delivered from neat Transcutol® P was significantly higher than from the other systems.
Transcutol® P is a safe and effective solubilizer of both hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds. It acts
as an enhancer by inducing a transient swelling of the hydrophilic regions of the stratum corneum,
rendering it permeable similar to fully hydrated skin. By diffusing into the skin layers, Transcutol® P
improves the drug solubility in the skin and its partitioning into the deeper hydrophilic regions of the
dermis (Osborne, 2018).
More information is provided in our Dermacare and Topical Drug Delivery brochures, available on
request.
Additionally, we offer:
✓ Regulatory, safety, and precedence of use assistance
✓ Enhancing formulation efficacy
✓ Expertise in sensorial properties
LIPIDS EXCIPIENTS FOR CANNABINOID DRUGS
The Benefits of Lipid Excipients in Alternative Drug Delivery Routes
A highly effective and yet unexploited approach to difficult drugs is mucosal delivery. The possibilities
include nasal, buccal, rectal, and vaginal routes of administration. In addition to circumventing
exposure to the GI tract where drug degradation may occur by digestive enzymes, bile sales and/or pH
related effects, this approach helps eliminate any first pass (hepatic elimination) risks for drugs like
cannabinoids.
Mucosal Delivery
Mucosal delivery is a unique alternative for administration of drug to patients with special needs.
Examples include children suffering from recurring seizures, patients unable to take oral medication,
and those in palliative care who may receive medicine as nasal sprays or suppositories.
Mucosal delivery is the fastest route of delivery, next to injectable / parenteral routes administration.
Compared to oral delivery, the benefits for incapacitated patients include:
✓ Rapid drug absorption and onset of action
✓ By-passing the hostile GI tract
✓ No risks of hepatic elimination
✓ No taste issue or emesis
Nasal or Buccal Sprays and Tinctures
Several products listed in Table 1, including Gattefossé solubilizers such as Lauroglycol™, Labrafac®
Lipophile WL 1349, Labrafil® M 1944 and Capryol™ series may be used alone or in combination,
to obtain drug solutions or dispersions in aqueous or microemulsion systems for use as sublingual
drops or nasal sprays.
Rectal and Vaginal Delivery
Solid lipid excipients, known in pharmacopoeia as “Hard fat” commonly constitute the “base” or the
medium for delivery of drugs in suppository (rectal) or pessary (vaginal). In order to meet the formulation
needs for different drugs, dose variations, mold types, and manufacturing speeds, Gattefossé has
developed a wide range of bases: namely the Suppocire® product line for rectal and the Ovucire® line
of excipients for vaginal routes of administration.
The Suppocire® bases consist of safe, well characterized, and globally referenced excipients which are
primarily composed of glycerol esters of fatty acids with varying chain length, degree of esterification,
hydrophilicity, and rate of crystallization. Within the Suppocire® line of products, there are unique series,
each designed to meet a specific set of formulation and manufacturing conditions. As an example the
Suppocire® M series are multipurpose vehicles for a wide range of drugs; the Suppocire® N series are
applied in high speed manufacturing environments; and Ovucire® are appropriate for the hydrophilic
vaginal environments.
The drug properties, intended dose, and mode of absorption are among the critical considerations
when selecting an appropriate base that will deliver the optimal physiochemical stability, dispersion
and release profile.
Having helped develop hundreds of marketed references over a 60-year span, our group has significant
and in-depth knowledge to share with the customers.
Advantages of Suppocire® and Ovucire® Series
✓ Drug delivery in high concentrations
✓ Faster absorption for a rapid onset of action
✓ Alternative for niche patient populations
✓ Bypassing the hostile GI tract
Lipid Excipients for Cannabinoid Drugs
Are you interested to receive more information or a sample? Just contact us


