Fundamental Aspects of Lipid-Based Excipients in Lipid-Based Product Development
Poor aqueous solubility of drugs is still a foremost challenge in pharmaceutical product development. The use of lipids in designing formulations provides an opportunity to enhance the aqueous solubility and consequently bioavailability of drugs. Pre-dissolution of drugs in lipids, surfactants, or mixtures of lipid excipients and surfactants eliminate the dissolution/dissolving step, which is likely to be the rate-limiting factor for oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. In this review, we exhaustively summarize the lipids excipients in relation to their classification, absorption mechanisms, and lipid-based product development. Methodologies utilized for the preparation of solid and semi-solid lipid formulations, applications, phase behaviour, and regulatory perspective of lipid excipients are discussed.
Continue reading here
List of lipid excipients used in the pharmaceutical product development USFDA IID- United States of Food and drug administration inactive ingredient database, USP—United States Pharmacopeia, NF—National formulary.
| Chemical Name | Functionalities | Example | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caprylocaproyl macrogol-8 glycerides | Solubilizer | SMEDDS | FDA IID |
| Hard Fat | Taste masking, Hot melt coating | HME, Melt granulation, NLCs | USFDA |
| Glycerol dibehenate | Sustained-release, Lubricant, API protection | SR tablet, SLN and NLCs | FDA IID |
| Glyceryl Monostearate | Lubricant, Emulsifier | Colloidal carriers | USFDA |
| Glycerol distearate | Sustained release, | SR Tablet, Lipid nanoparticles, Hot melt coating | FDA IID |
| Lubricant, Taste-masking | |||
| Glyceryl Monocaprylate | Permeability enhancer, Emulsifier, Solubilizer | SEDDS, Nanoparticles [13] | USP/NF |
| Propylene Glycol Monocaprylate | Emulsifier, Solubilizer | SEDDS, Nanoparticles | USFDA |
| Glycerol Monocaprylocaprate | Solubilizer, penetration enhancer | SNEDDS | USFDA |
| Succinic Triglycerides | Super fatting | Creams | USFDA |
| Agent | |||
| Lauroyl macrogol-32 glycerides | Bioavailability enhancer | Hard gelatin capsule (SNEDDS, SMEDDS), Mixed micelles | FDA IID |
| Oleoyl macrogrol-32 glyceride | Bioavailability enhancer, Solubilizer | Oral solutions, SMEDDS | FDA IID |
| Polyglyceryl-3 dioleate | Surfactant | Niosomes | FDA IID |
| Propylene glycol dicaprylocaprate | Oily vehicle | Emulsions and Nanocapsules | FDA IID |
| Trimyristin | Controlled release, Lubricant, taste masking | SLNs [20], HME, SEDDS, SLMs | USFDA |
| Tristearin/Glyceryl Tristearate | Controlled release, Lubricant, lipid carrier | HME, Hot melt coating as a taste masking agent, SMEDDS and SLMs | USFDA |
| Glyceryl Caprylate | Permeability enhancer, Emulsifier, Solubilizer | SMEDDS | IIG/USFDA |
| Polyoxyl stearate | Bioavailability enhancer | (SNEDDS, SMEDDS) and Solid dispersion | FDA IID |
| Stearoylmacrogol-32 glyceride | Bioavailability enhancer | Solid dispersion | FDA IID |
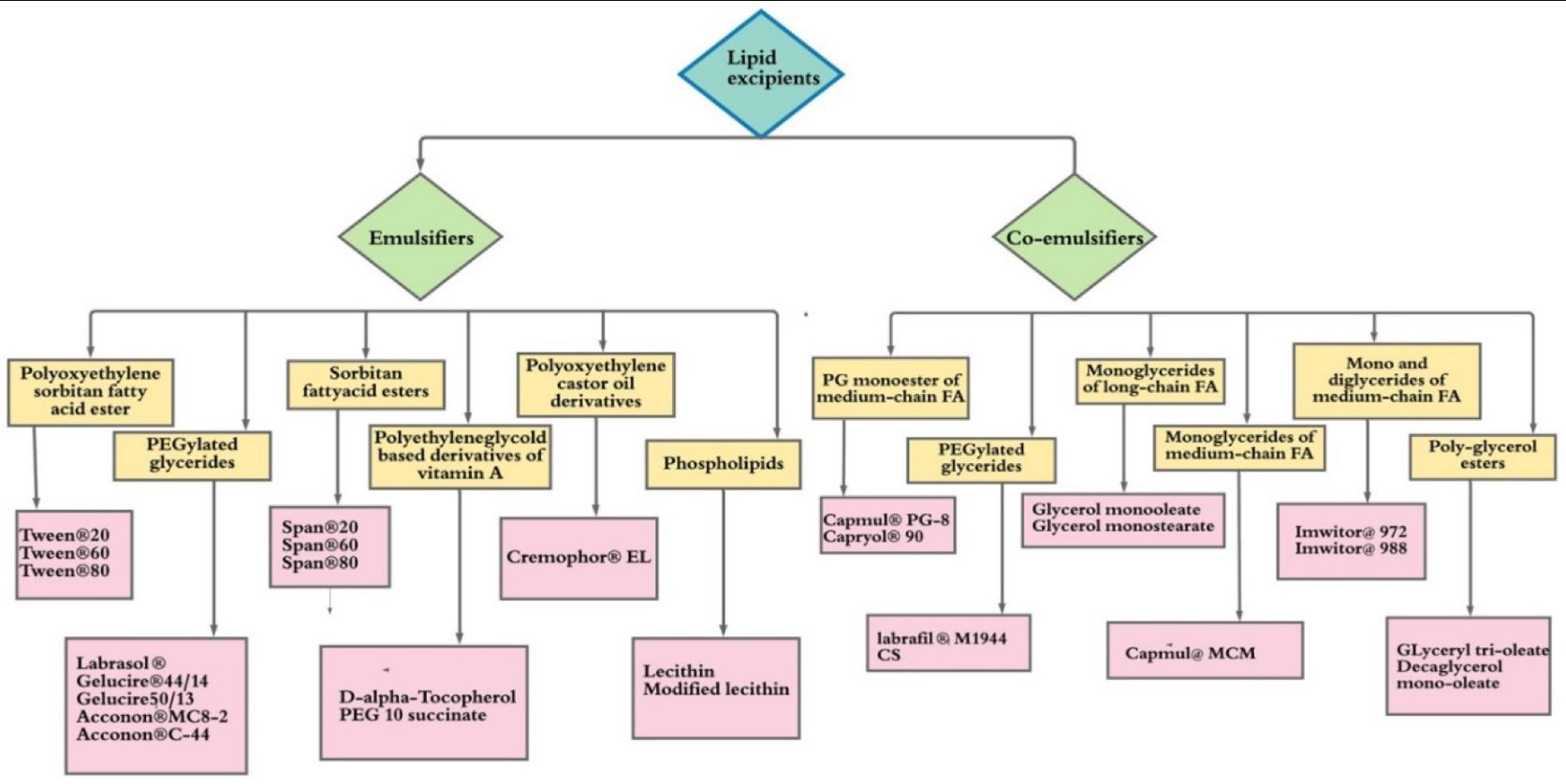
Overview Lipd Excipients as of this article
| Type | Group | Excipient |
|---|---|---|
| Emulsifier | Polyoxethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester | Tween 20 |
| Emulsifier | Polyoxethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester | Tween 60 |
| Emulsifier | Polyoxethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester | Tween 80 |
| Emulsifier | PEGylated glycerides | Labrasol |
| Emulsifier | PEGylated glycerides | Gelucire 44/14 |
| Emulsifier | PEGylated glycerides | Gelucire 50/13 |
| Emulsifier | PEGylated glycerides | Acconon MC8-2 |
| Emulsifier | PEGylated glycerides | Acconon C-44Acconon C-44 |
| Emulsifier | Sorbitan fattyacid esters | Span 20 |
| Emulsifier | Sorbitan fattyacid esters | Span 60 |
| Emulsifier | Sorbitan fattyacid esters | Span 80 |
| Emulsifier | Polyethyleneglycold based derivatives of vitamin A | D-alpha-Tocopherol PEG 10 succinate |
| Emulsifier | Polyoxythelyne castor oil derivatives | Cremophor EL |
| Emulsifier | Phospholipids | Lecithin modified lecithin |
| Co-Emulsifiier | PG monoester of medium-chain FA | Capmul PG-8 |
| Co-Emulsifiier | PG monoester of medium-chain FA | Capryol 90 |
| Co-Emulsifiier | PEGylated glycerides | Labrafil M1944 |
| Co-Emulsifiier | Monoglycerides of long-chain FA | Glycerol monooleate |
| Co-Emulsifiier | Monoglycerides of long-chain FA | Glycerol monostearate |
| Co-Emulsifiier | Monoglycerides of medium-chain FA | Capmul MCM |
| Co-Emulsifiier | Mono and diglycerides of medium chain FA | Imwitor 972 |
| Co-Emulsifiier | Mono and diglycerides of medium chain FA | Imwitor 988 |
| Co-Emulsifiier | Poly-glyercol esters | Glyeceryl tri-oleate Decaglycerol mono-oleate |
About this article: Nakmode, D.; Bhavana, V.; Thakor, P.; Madan, J.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, S.B.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Bansal, K.K.; Mehra, N.K. Fundamental Aspects of Lipid-Based Excipients in Lipid-Based Product Development. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040831

