Fused deposition modelling for the development of antiplatelet materials for cardiovascular applications

The 12th APV PBP World Meeting took place from 28 – 31 March 2022 in Rotterdam. There was a poster section at the event where really interesting scientific posters were presented. Therefore we asked the presenting scientists if we could share their work in addition online with the Pharma Excipients community.
As many scientists send us their posters we will show several posters of the PBP Poster Session stepwise over the next weeks.
The next poster in our series was presented by Juan Domínguez-Robles, School of Pharmacy, Queen’s University Belfast:
(click on the poster to enlarge it)
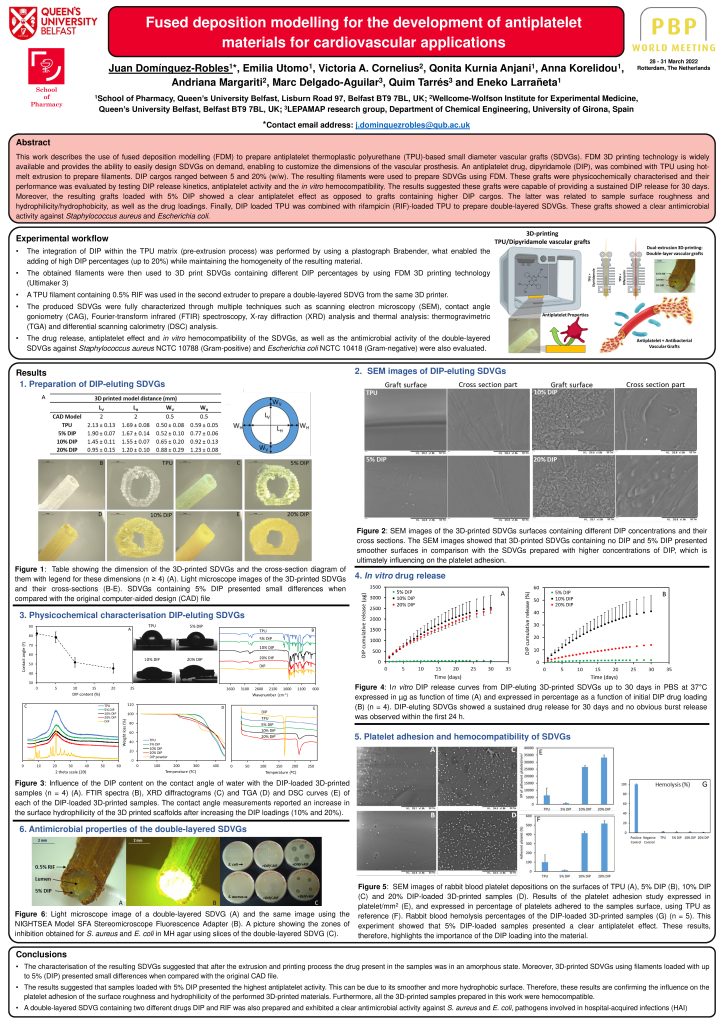
Download the full research poster as PDF: Fused deposition modelling for the development of antiplatelet
Abstract
This work describes the use of fused deposition modelling (FDM) to prepare antiplatelet thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)-based small diameter vascular grafts (SDVGs). FDM 3D printing technology is widely available and provides the ability to easily design SDVGs on demand, enabling to customize the dimensions of the vascular prosthesis. An antiplatelet drug, dipyridamole (DIP), was combined with TPU using hotmelt extrusion to prepare filaments. DIP cargos ranged between 5 and 20% (w/w). The resulting filaments were used to prepare SDVGs using FDM. These grafts were physicochemically characterised and their performance was evaluated by testing DIP release kinetics, antiplatelet activity and the in vitro hemocompatibility. The results suggested these grafts were capable of providing a sustained DIP release for 30 days.
Moreover, the resulting grafts loaded with 5% DIP showed a clear antiplatelet effect as opposed to grafts containing higher DIP cargos. The latter was related to sample surface roughness and hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity, as well as the drug loadings. Finally, DIP loaded TPU was combined with rifampicin (RIF)-loaded TPU to prepare double-layered SDVGs. These grafts showed a clear antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
Authors:
Juan Domínguez-Robles1*, Emilia Utomo1, Victoria A. Cornelius 2, Qonita Kurnia Anjani 1, Anna Korelidou 1,
Andriana Margariti 2, Marc Delgado-Aguilar 3, Quim Tarrés 3 and Eneko Larrañeta 1
1 School of Pharmacy, Queen’s University Belfast, Lisburn Road 97, Belfast BT9 7BL, UK; 2 Wellcome-Wolfson Institute for Experimental Medicine, Queen’s University Belfast, Belfast BT9 7BL, UK; 3 LEPAMAP research group, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Girona, Spain
See more PBP World meeting posters:

