Development of Osthole-Loaded Microemulsions as a Prospective Ocular Delivery System for the Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments
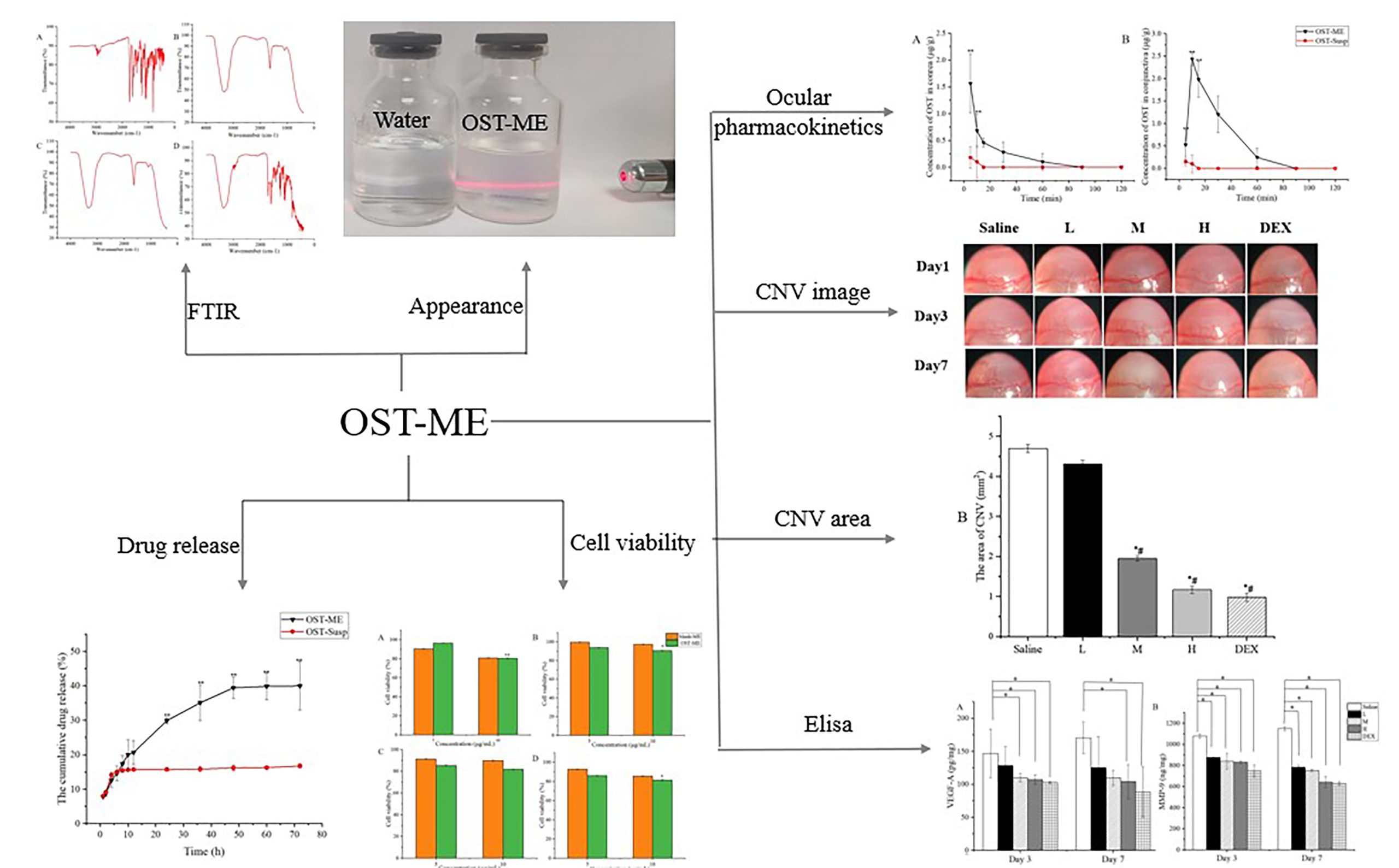
Osthole (OST), a natural coumarin compound, has shown a significant inhibitory effect on corneal neovascularization (CNV). But, its effect on treating CNV is restricted by its water insolubility. To overcome this limitation, an OST-loaded microemulsion (OST-ME) was created to improve the drug’s therapeutic effect on CNV after topical administration. The OST-ME formulation comprised Capryol-90 (CP-90), Cremophor® EL (EL-35), Transcutol-P (TSP) and water, and sodium hyaluronate (SH) was also included to increase viscosity. The OST-ME had a droplet size of 16.18 ± 0.02 nm and a low polydispersity index (0.09 ± 0.00). In vitro drug release from OST-ME fitted well to the Higuchi release kinetics model. Cytotoxicity assays demonstrated that OST-ME was not notably toxic to human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs), and the formulation had no irritation to rabbit eyes. Ocular pharmacokinetics studies showed that the areas under the concentration–time curves (AUC0-t) in the cornea and conjunctiva were 19.74 and 63.96 μg/g*min after the administration of OST-ME, both of which were 28.2- and 102.34-fold higher than those after the administration of OST suspension (OST-Susp). Moreover, OST-ME (0.1%) presented a similar therapeutic effect to commercially available dexamethasone eye drops (0.025%) on CNV in mouse models. In conclusion, the optimized OST-ME exhibited good tolerance and enhanced 28.2- and 102.34-fold bioavailability in the cornea and conjunctiva tissues compared with suspensions in rabbit eyes. The OST-ME is a potential ocular drug delivery for anti-CNV.
4.1. Materials
Osthole (OST), isopropyl myristate (IPM), and monoolein were provided by Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) were purchased from Yunhong Chemical Preparation Excipients Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Ethyl oleate and triacetin were obtained from J&K Scientific Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Oleic acid was provided by Tokyo Chemical Industries Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Propylene glycol dicaprylate (PGD) and castor oil were provided by Hunan Er-Kang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Changsha, China). PEG400 was obtained from Solarbio Life Science (Beijing, China). EL-35 was obtained from Shanghai Puzhen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Kolliphor HS-15 (HS-15) was obtained from BASF SE (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Tween-80 (TW-80) was obtained from Sichuan Jinshan Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Guangyuan, China). TSP and CP-90 were acquired from Gattefosse (Saint-Priest, France). Glycerin was provided by Huikang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Lishui, Zhejiang, China). Sodium hyaluronate (SH) was obtained from Furuida Biochemical Co., Ltd. (Qingdao, Shandong, China). A Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was acquired from APExBIO (Houston, TX, USA). Mice MMP-9 and VEGF-A enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were acquired from Elabscience Biotechnology (Wuhan, China). Dexamethasone (DEX) sodium phosphate solution were provided by Huaqing Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Xinxiang, China).
Download the full research paper as PDF here: Development of Osthole-Loaded Microemulsions as a Prospective Ocular Delivery System for the Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments
or read it here
Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ji, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Development of Osthole-Loaded Microemulsions as a Prospective Ocular Delivery System for the Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1342.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101342

