Evaluation of Oromucosal Natural Gum-Based Emulgels as Novel Strategy for Photodynamic Therapy of Oral Premalignant Lesions
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) recently has been shown as a promising option in the treatment of premalignant lesions of the soft oral tissues. Effective delivery of photosensitizer is challenging due to poor drug adherence to the oromucosal epithelium. In the present work, emulgels composed of natural polysaccharide gums (tragacanth, xanthan and gellan) were evaluated as novel oromucosal platforms of delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) for PDT. Apart from mucoadhesive and textural analysis, the specific steps involved studies on drug penetration behavior and safety profile using a three-dimensional human oral epithelium model (HOE). All designed emulgels presented greater mucoadhesiveness when compared to commercial oromucosal gel.
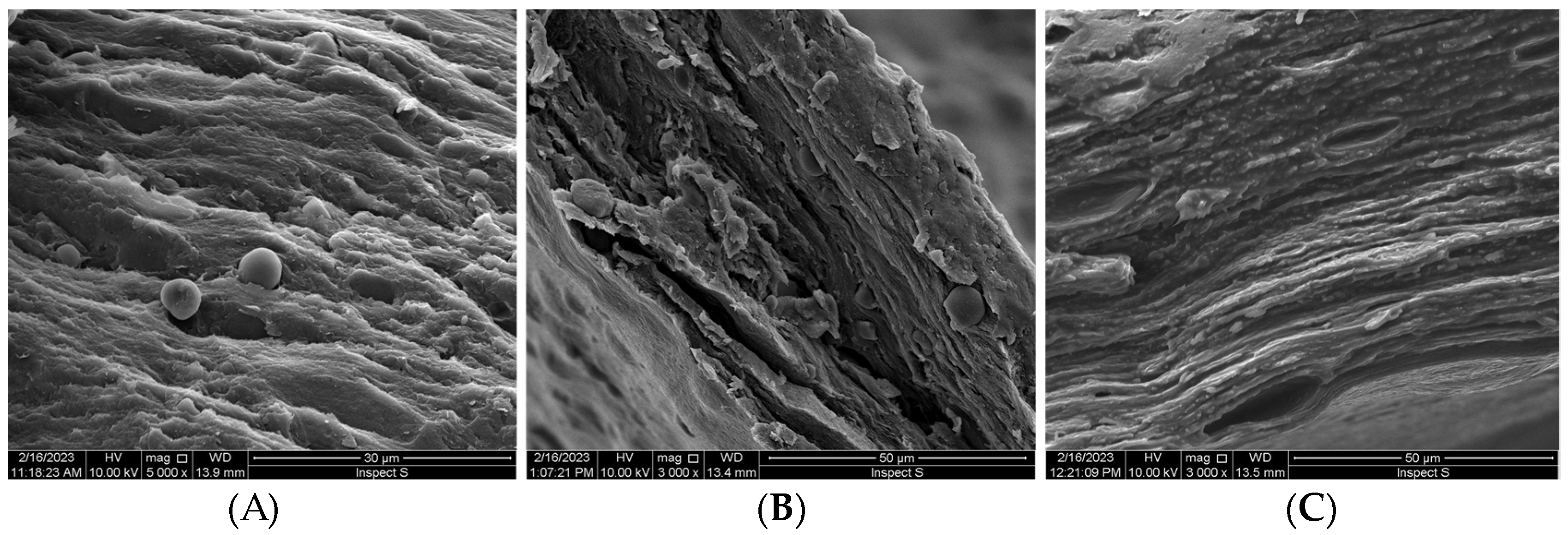
Incorporation of ALA affected textural properties of emulgels, and tragacanth/xanthan formulation with greater hardness and cohesiveness exhibited a protective function against the mechanical tongue stress. Permeability studies revealed that ALA is capable of penetrating across oromucosal epithelium by passive transport and all formulations promoted its absorption rate when compared to a commercial topical product with ALA. Importantly, the combination of tragacanth and xanthan profoundly enhanced photosensitizer retention in the buccal epithelium.
Tested samples performed negligible reduction in cell viability and moderately low IL-1β release, confirming their non-irritancy and compatibility with HOE. Overall, the presented findings indicate that tragacanth/xanthan emulgel holds promise as an oromucosal ALA-carrier for PDT strategy.
Download the full article as PDF here Evaluation of Oromucosal Natural Gum-Based Emulgels as Novel Strategy for Photodynamic Therapy of Oral Premalignant Lesions
or read it here
Materials
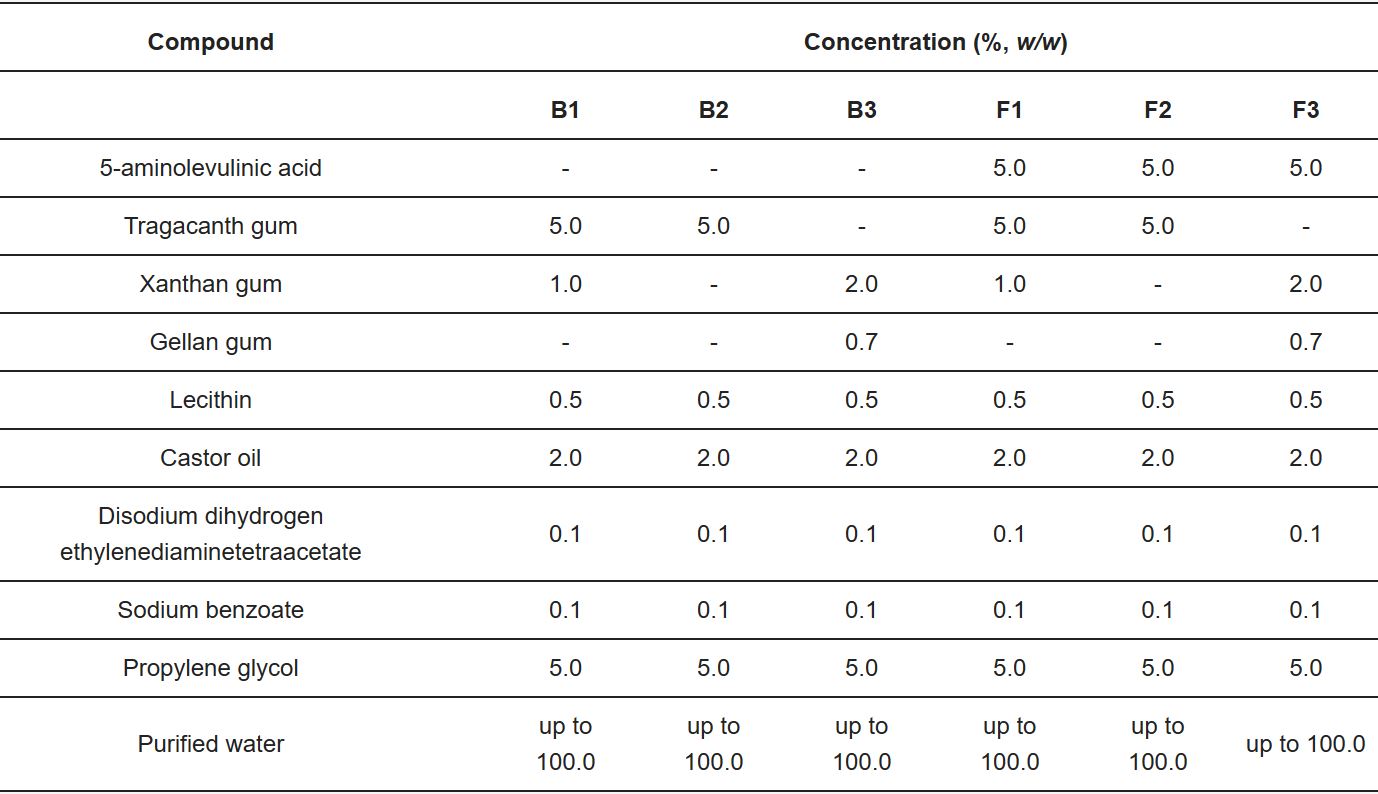
Tragacanth from Astragalus gummifer, composed primarily of tragacanthin and bassorin with average viscosity of 1% aqueous dispersion 200 cPa·s at 25 °C and XA (average viscosity of 1% aqueous dispersion 1500 cPa·s at 25 °C) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Gellan gum (Kelcogel CG-HA) was obtained from CP Kelco (Atlanta, GA, USA). The simulated saliva fluid (SSF), composed of 0.1 M disodium hydrogen phosphate and 0.1 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate, was prepared according to [21]. Commercial topical gel with ALA Ameluz (serial number 04150094218327) composed of ALA, disodium phosphate isopropyl alcohol, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, water, sodium benzoate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, xanthan gum, soybean phosphatidylcholine and medium chains triglyceride was purchased from Biofronterra Pharma GmbH (Leverkusen, Germany). Reference oromucosal gel Anaftin (serial number 270141) composed of water, polyvinylpyrrolidone, maltodextrin, propylene glycol, PEG-40 hydrogenated castor oil, xanthan gum, potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate, sodium hyaluronate, benzalkonium chloride, disodium dihydrogen ethylenediaminetetraacetate, sodium saccharin, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate and Aloe barbadensis was from Alliance Pharma Srl (Milan, Italy). All the other chemicals used in the studies are summarized in Table 1. Freshly excised porcine buccal mucosa was obtained from the veterinary service of a local slaughterhouse (Turośń Kościelna, Poland). Tissue specimens were preserved in the isotonic saline solution, frozen at −20 °C directly after killing the animal and kept no longer than 30 days. Prior to the test, tissue was thawed at ambient conditions, cut into pieces, and microscopically checked for tissue integrity.
Szymańska, E.; Potaś, J.; Baranowski, M.; Czarnomysy, R.; Sulewska, M.E.; Basa, A.; Pietruska, M.; Bielawski, K.; Winnicka, K. Evaluation of Oromucosal Natural Gum-Based Emulgels as Novel Strategy for Photodynamic Therapy of Oral Premalignant Lesions. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15102512
Read more on Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODTs) here:


