Tablet Disintegratability: Sensitivity of Superdisintegrants to Temperature and Compaction Pressure
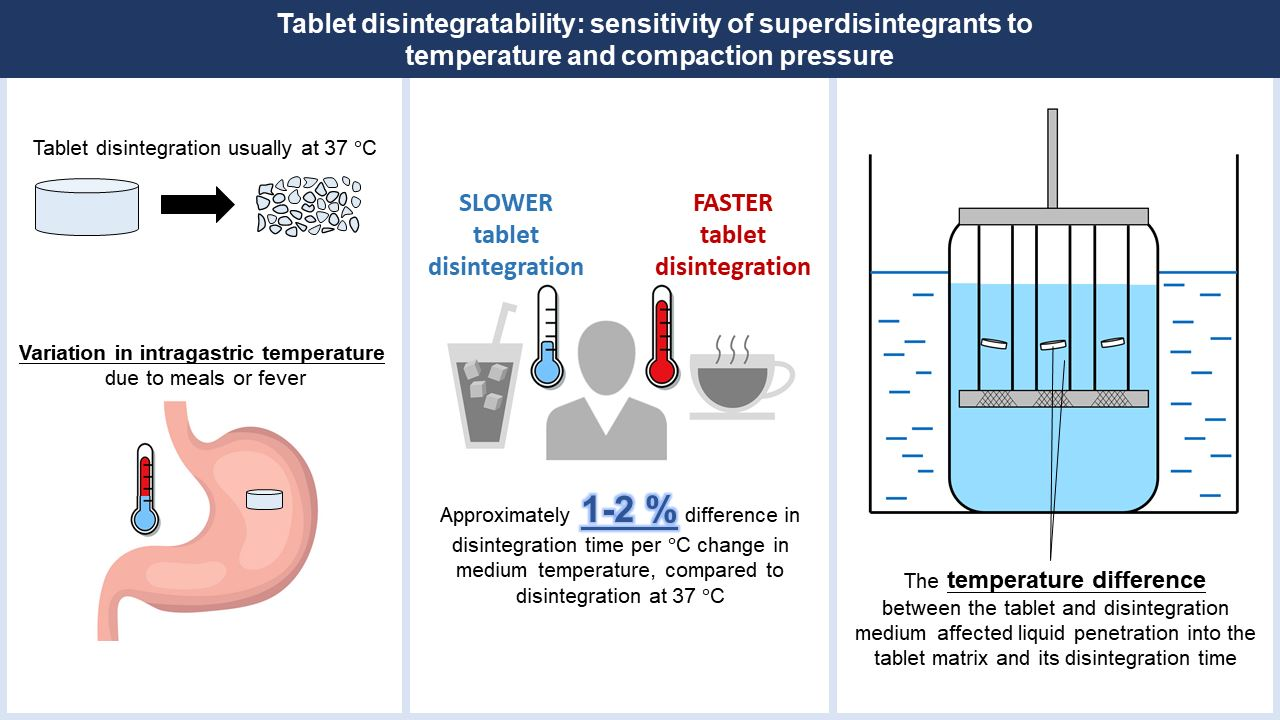
Tablet disintegration is an important pre-requisite for drug dissolution and absorption. The disintegration test is typically conducted at 37 °C, but the intragastric temperature may vary due to meals or fever. This study investigated the effects of temperature and compaction pressure on tablet disintegratability to gain deeper insights into superdisintegrant sensitivity and function. Tablets with either sodium starch glycolate or crospovidone as disintegrant were prepared at various compaction pressures and subjected to the disintegration test using different medium temperatures.
Preheating of tablets was also employed to establish instant temperature equilibrium between the tablet and the disintegration medium. Liquid penetration and disintegration were faster as the medium temperature increased or compaction pressure decreased. Swelling or strain recovery disintegrants exhibited similar sensitivity to variations in the medium temperature. Preheating of the tablets resulted in slower disintegration, but this effect was reversible upon cooling, hence the slower disintegration was unlikely to be attributed to changes in the disintegrant physical state.
The temperature difference between the tablet and the disintegration medium likely affected the rate of fluid flow into tablets and influenced disintegration. Understanding disintegrant temperature sensitivity would help to avoid unacceptable fluctuations in disintegration due to temperature variations. The temperature difference effect could also be harnessed to boost disintegrant performance.
Download the full article as PDF here Tablet Disintegratability_Sensitivity of Superdisintegrants to Temperature and Compaction Pressure
or read it here
Materials
Sodium starch glycolate (SSG; Primojel, DFE Pharma, Goch, Germany) and crospovidone (XPVP; Kollidon CL, BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) were the superdisintegrants employed in this study. Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCP; Emcompress, JRS Pharma, Rosenberg, Germany) was used as the filler. DCP was chosen as it is a commonly used diluent that does not exhibit aqueous solubility or strong wicking, which could be influenced by the disintegration medium temperature and confound the investigation. Magnesium stearate (M-125, Productos Metalest, Zaragoza, Spain) was used as the lubricant.
Preparation of Tablets
Tablets were produced using a compaction simulator (STYL’One, MEDELPHARM, Beynost, France) using 14-mm flat-face punches and die (Natoli Engineering, Saint Charles, MO, USA). The tablet formulation comprised 2%, w/w SSG or XPVP, 97%, w/w DCP, and 1%, w/w magnesium stearate. Tablets weighing 1 g each were compacted at 65, 97 and 130 MPa, and all tablets were aged for at least 24 h prior to their use for characterization tests.
Zheng, A.Y.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Tablet Disintegratability: Sensitivity of Superdisintegrants to Temperature and Compaction Pressure. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122725
Read more on Magnesium Stearate as a pharmaceutical excipient here:


