In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of the Transdermal Gel Formulation of Desloratadine for Prevention of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
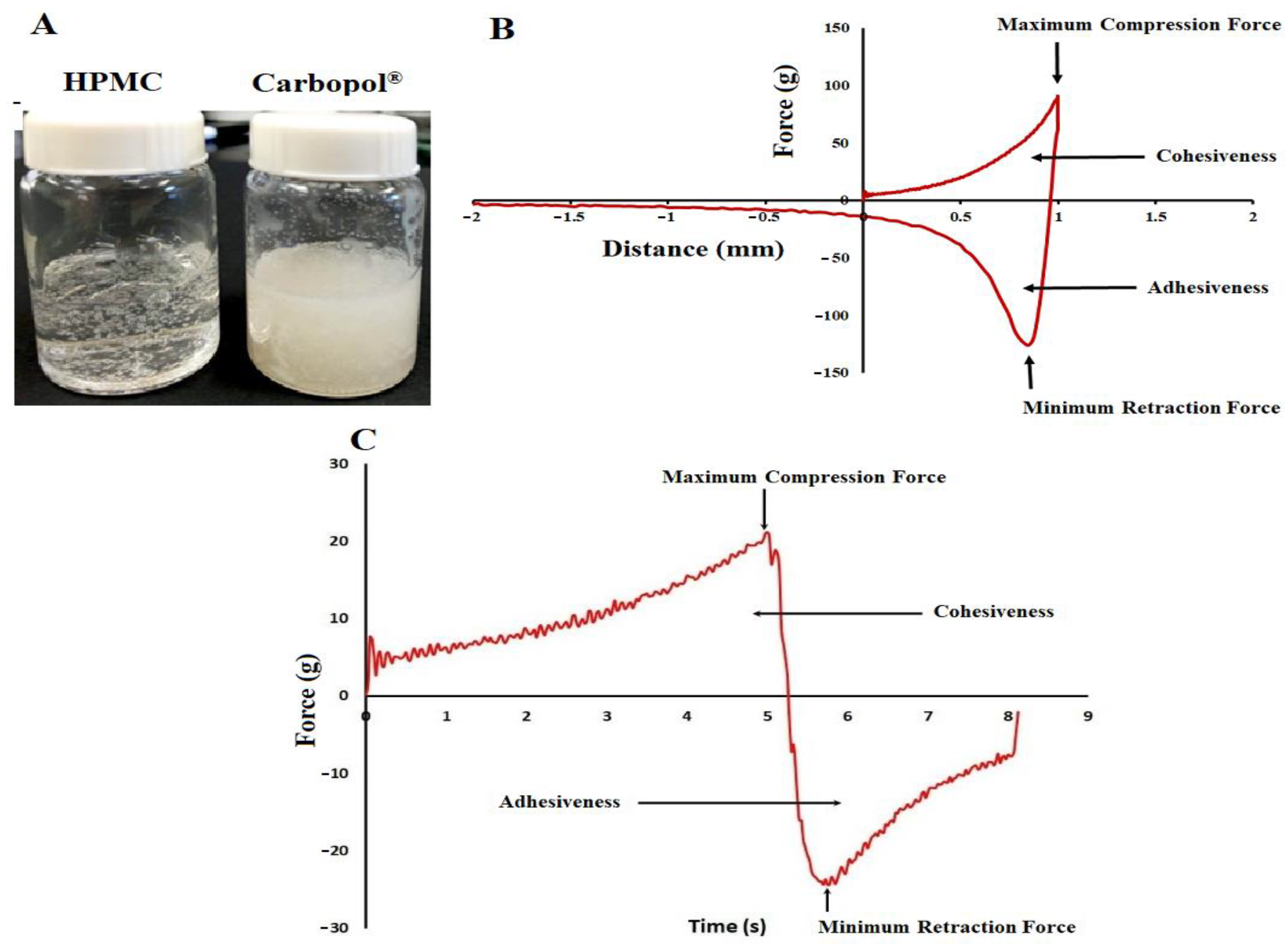
Chronic use of antihistamines can induce abnormalities in lipid absorption with potential excessive accumulation of lipids in the mesentery that can lead to the development of obesity and a metabolic syndrome. The focus of the present work was to develop a transdermal gel formulation of desloratadine (DES) to prevent/reduce obesity and metabolic syndromes. Nine formulations were prepared to contain hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (2–3%), DES (2.5–5.0%), and Transcutol® (15–20%). The formulations were evaluated for cohesive and adhesive properties, viscosity, drug diffusion through synthetic and pig ear skin, and pharmacokinetics in New Zealand white rabbits. Drug permeation was faster through the skin compared to synthetic membranes. The drug had good permeation, as indicated by very short lag time (0.08–0.47 h) and high flux (59.3–230.7 μg/cm2.h). The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) of transdermal gel formulations were 2.4 and 3.2 fold that of the Clarinex tablet formulation. In conclusion, as indicated by the higher bioavailability, transdermal gel formulation of DES may decrease the dose of the drug, compared to commercial formulation. It has the potential to reduce or eliminate metabolic syndromes associated with oral antihistamine therapy.
Download the full article as PDF here In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of the Transdermal Gel Formulation of Desloratadine for Prevention of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
or read it here
Materials
DES was purchased from Lide Pharmaceuticals Limited, Nanjing, China. Polyethersulfone membrane (Strat-MTM, Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany). HPMC (BenecelTM K100M PHARM), Carbopol® 934P NF, Carbopol® 980, Transcutol® HP, and HPBCD (Kleptose, oral grade) were obtained from Ashland Specialty Ingredients (Wilmington, DE, USA); Lubrizol Advanced Materials, Inc., (Cleveland, OH, USA); Gattefosse SAS (Nanterre, France); and Roquette America Inc. (Keokuk, IA, USA), respectively. Deuterated DES (DES-d4) was obtained from Toronto Research Chemicals, Ontario, Canada. Heparinized rabbit plasma was purchased from BioChemed Services, Winchester, VA, USA. PEG 400, PG, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, orthophosphoric acid, sodium hydroxide, formic acid, and methanol were purchased from Fisher Scientific, Asheville, NC, USA. All reagents were of analytical grade and were used as received. In-house water (18 MU.cm, Millipore Milli-Q Gradient A-10 water purification system) was used in this work.
Mohamed, E.M.; Dharani, S.; Khuroo, T.; Hamed, R.; Khan, M.A.; Rahman, Z. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of the Transdermal Gel Formulation of Desloratadine for Prevention of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040578
Read more on Disintegrants – Pharmaceutical Excipients here:


