Topically applied lipid-containing emulsions based on PEGylated emulsifiers: Formulation, characterization, and evaluation of their impact on skin properties ex vivo and in vivo
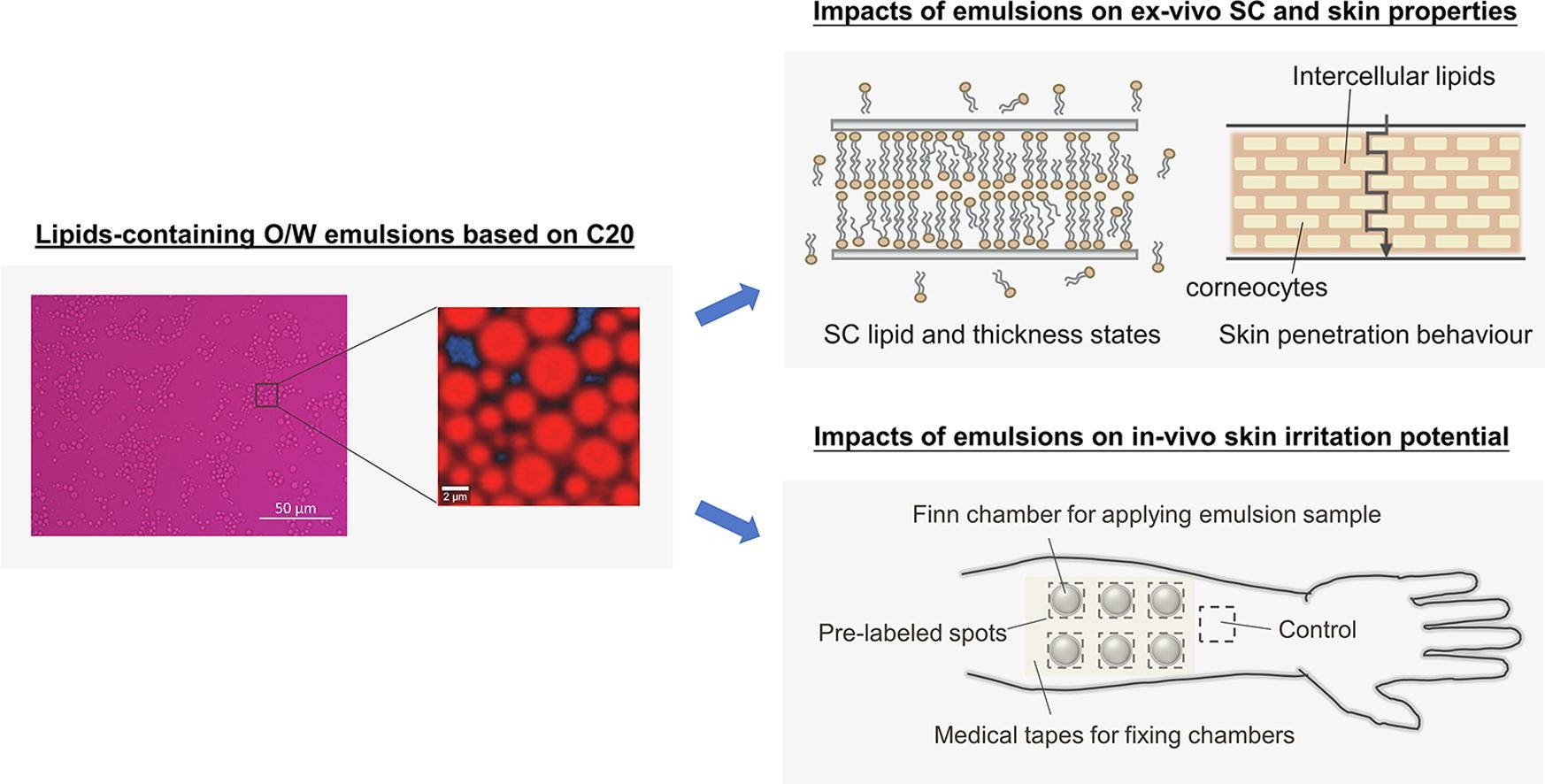
PEGylated emulsifiers have been largely used in topical formulations for skin research. They have been a continuous study focus in our group as well. According to our previous studies, severe interruptions of the skin barrier were observed with certain types of emulsifiers. To restore the skin barrier function and counteract the effects of emulsifiers, we considered topically delivering lipids into the lipid matrix of the SC. Herein, PEG-20 cetyl ether (C20) -based oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions were developed owing to the stronger interactions of C20 with skin.
The lipids containing ceramides (Cers), palmitic acids (PA), and cholesterol with different ratios and combinations were merged into the base emulsion. PEG-40 stearyl ether (S40)-based emulsion was used as a reference as S40 showed negligible impact on SC lipids. The evaluations were conducted ex vivo with confocal Raman spectroscopy (CRS) regarding the SC lipid, SC thickness, and skin penetration properties. In parallel, the in vivo irritation studies were also implemented including the transepidermal-water-loss (TEWL), skin hydration, and erythema index.
The results indicated less SC lipid extraction of topically delivered lipids on ex vivo porcine skin with the addition and ratio of incorporated Cers influencing the extent of formulations counteracting the skin interruption by C20. The ex vivo penetration study showed a similar trend in drug penetration depths. In regards to the in vivo studies, TEWL was demonstrated to be suitable for differentiating the impact on skin barrier properties. The in vivo observations were generally correlated with the ex vivo results. The exact findings in this research can lead us to a better selection of applied lipid components and compositions. Future research will elucidate which type of Cer was predominantly extracted by C20, advancing future formulation development.
Materials
Caffeine was purchased from Ceasar & Loretz GmbH (D-Hilden, Germany). Emulsifiers of PEG-20 cetyl ether (C20) and PEG-40 stearyl ether (S40) were obtained from Croda GmbH (Nettetal, Germany). Carbopol® 971P NF polymer was obtained from Lubrizol Corp. (Ohio, USA). Medium-chain triglyceride (Myritol 318, MCT) was achieved from BASF (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Palmitic acid and cholesterol were purchased from Alfa Aesar GmbH & Co KG (Karlsruhe, Germany). Ceramide NP (Cer NP) was obtained from Alexmo cosmetics GmbH (Stuhr, Germany) and ceramide VI (Ceramide AP, Cer AP) was bought from Evonik Industries AG (Essen, Germany). Parafilm® was from Bemis Company Inc., (Oshkosh, WI, USA). Trypsin type II-S (lyophilized powder) and trypsin inhibitor (lyophilized powder) were provided by Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH (Steinheim, Germany). Sodium chloride, disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and potassium chloride were of European Pharmacopoeia grade. All aqueous solutions were prepared with ultra-pure water (Elga Maxima, High Wycombe, UK).
Yali Liu, Tanja Ilić, Ivana Pantelic, Snežana Savić, Dominique Jasmin Lunter, Topically applied lipid-containing emulsions based on PEGylated emulsifiers: Formulation, characterization, and evaluation of their impact on skin properties ex vivo and in vivo, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 626, 2022, 122202, ISSN 0378-5173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122202

