Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy
In this study, an amorphous solid dispersion containing the poorly water-soluble drug, bisacodyl, was prepared by hot-melt extrusion to enhance its therapeutic efficacy. First, the miscibility and interaction between the drug and polymer were investigated as pre-formulation strategies using various analytical approaches to obtain information for selecting a suitable polymer.
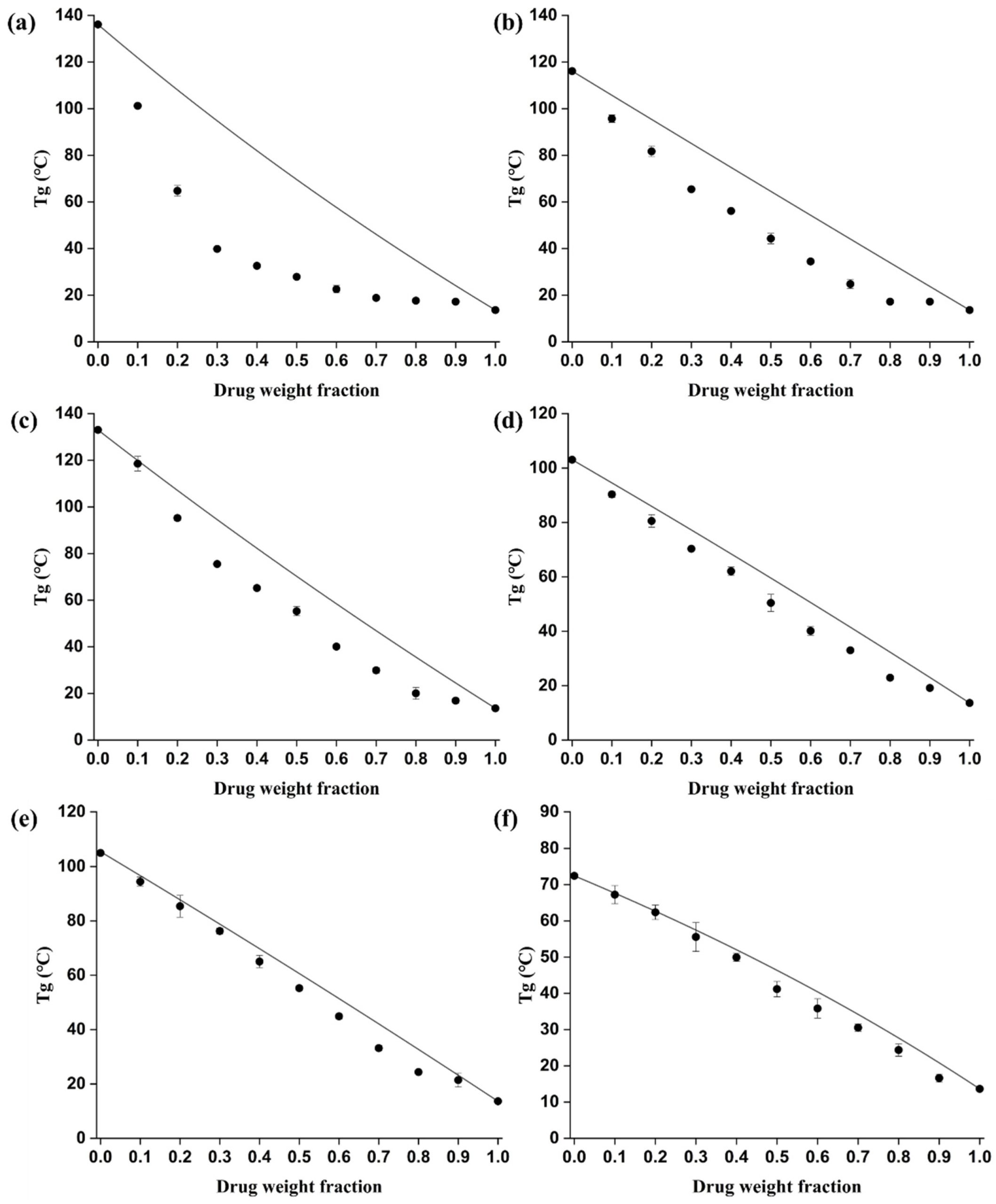
Based on the calculation of the Hansen solubility parameter and the identification of the single glass transition temperature (𝑇𝑔), the miscibility between bisacodyl and all the investigated polymers was confirmed. Additionally, the drug–polymer molecular interaction was identified based on the comprehensive results of dynamic vapor sorption (DVS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), Raman spectroscopy, and a comparison of the predicted and experimental values of 𝑇𝑔.
In particular, the hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)-based solid dispersions, which exhibited large deviation between the calculated and experimental values of 𝑇𝑔 and superior physical stability after DVS experiments, were selected as the most appropriate solubilized bisacodyl formulations due to the excellent inhibitory effects on precipitation based on the results of the non-sink dissolution test.
Furthermore, it was shown that the enteric-coated tablets containing HPMC–bisacodyl at a 1:4 ratio (w/w) had significantly improved in vivo therapeutic laxative efficacy compared to preparations containing un-solubilized raw bisacodyl in constipation-induced rabbits. Therefore, it was concluded that the pre-formulation strategy, using several analyses and approaches, was successfully applied in this study to investigate the miscibility and interaction of drug–polymer systems, hence resulting in the manufacture of favorable solid dispersions with favorable in vitro and in vivo performances using hot-melt extrusion processes.
2.1. Materials
Bisacodyl (0.999 in mass fraction purity) was kindly provided by Dong-A ST Co., Ltd. (Seoul, Republic of Korea). Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC, SSL grade) was obtained from Nippon Soda Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC, Pharmacoat® 603), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS, AQOAT® MG), and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP, HP-50) were acquired from Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Polyvinylpyrrolidone K12 (PVP K12, Kollidon® K12), polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate copolymer (PVP VA64, Kollidon® VA64), and polyvinyl caprolactam–polyvinyl acetate–polyethylene glycol graft copolymer (Soluplus®) were supplied by BASF Co., Ltd. (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Ultrapure water was obtained using the Milli-Q purification system (Millipore, Molsheim, France). Other chemicals and solvents used in this study were of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or reagent grade.
| Content | F1 (mg/Tablet) | F2 (mg/Tablet) |
|---|---|---|
| Tablet | ||
| Raw bisacodyl | 2.5 | |
| Hot-melt-extruded solid dispersions (Bisacodyl:HPMC = 1:4 w/w) | 12.5 | |
| Aerosil 200 | 10 | 10 |
| Avicel PH102 | 40 | 30 |
| HPC-EXF | 5 | 5 |
| Kollidon CL | 5 | 5 |
| Magnesium stearate | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Enteric-coating layer | ||
| Eudragit L100 | 13.75 | 13.75 |
| Eudragit S100 | 13.75 | 13.75 |
| TEC | 2.25 | 2.25 |
| Talc | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| Total weight of enteric-coated tablet | 100 | 100 |
Download the full study as PDF here: Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy
or read it here
Lee, S.-K.; Ha, E.-S.; Park, H.; Kang, K.-T.; Jeong, J.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Baek, I.-h.; Kim, M.-S. Preparation of Hot-Melt-Extruded Solid Dispersion Based on Pre-Formulation Strategies and Its Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2704.
https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122704

