Lipid-coated nanocrystals of paclitaxel as dry powder for inhalation: Characterization, in-vitro performance, and pharmacokinetic assessment
Abstract
Background
Nanocrystals can be produced as a dry powder for inhalation (DPIs) to deliver high doses of drug to the lungs, owing to their high payload and stability to the shear stress of aerosolization force. Furthermore, lipid-coated nanocrystals can be formulated to improve the drug accumulation and retention in lung.
Highlights
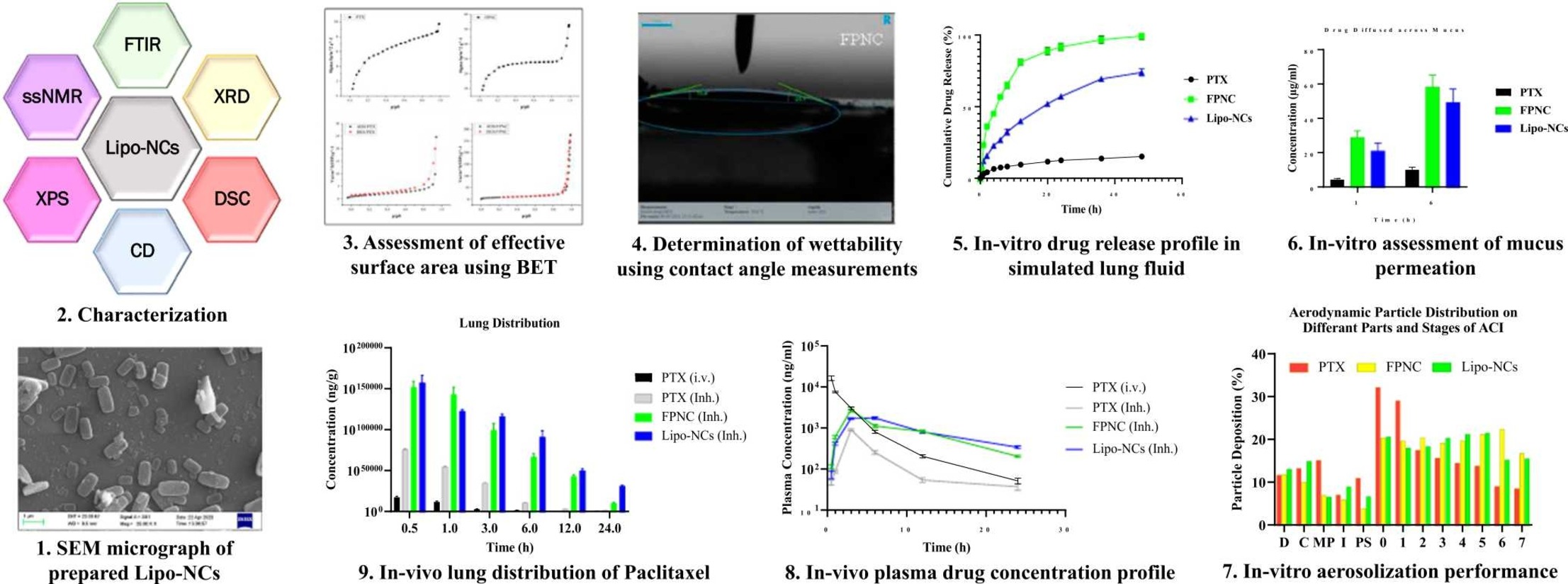
- Sub-micron sized PTX loaded Lipo-NCs were prepared for pulmonary delivery.
- The NCs exhibited improved dissolution due to ∼10-fold effective surface area.
- Aerosolization performance revealed deep lung distribution capability of NCs.
- Lipo-NCs showed superior lung accumulation with minimal systemic distribution.
- Lipo-NCs is ideal for pulmonary delivery of PTX in localized lung cancer therapy.
Objective
The present work involved the fabrication of paclitaxel nanocrystals using hydrophilic marine biopolymer fucoidan as a stabilizer. Thereafter, fabricated nanocrystals (FPNC) were surface-modified with phospholipid to give lipid-coated nanocrystals (Lipo-NCs).
Methods
The nanocrystals were fabricated by antisolvent crystallization followed by the probe sonication. The lipid coating was achieved by thin film hydration followed ultrasonic dispersion technique. Prepared nanocrystals were lyophilized to obtain a dry powder of FPNC and Lipo-NCs, used later for physicochemical, microscopic, and spectroscopic characterization to confirm the successful formation of desired nanocrystals. In-vitro and in-vivo investigations were also conducted to determine the role of nanocrystal powder in pulmonary drug delivery.
Results
Lipo-NCs exhibited slower drug release, excellent flow properties, good aerosolization performance, higher drug distribution, and prolonged retention in the lungs compared to FPNC and pure PTX.
Conclusion
Lipid-coated nanocrystals can be a novel formulation for the maximum localization of drugs in the lungs, thereby enhancing therapeutic effects and avoiding systemic side effects in lung cancer therapy.
Read more here
Materials
Paclitaxel (USP, 98–100%) gift sample was obtained from MSN Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., Unit II, Sy No:50, Kardanur, Medak (Dist.), Telangana, India. Fucoidan (Undaria pinnatifida) of medicine grade (98% fucoidan) was gifted by Nutra Green Biotechnology, Co., Ltd. Shanghai Lvshang Biotechnology, Shanghai-200129, China. Vitamin E TPGS NF Grade was obtained as a gift sample from Antares Health Products, St. Charles, USA. Gift sample of soybean lecithin (SLec.) was received from Lipoid, GmbH.
Manish Kumar, Abhishek Jha, Kanchan Bharti, Manjit Manjit, Pradnya Kumbhar, Vividha Dhapte-Pawar, Brahmeshwar Mishra, Lipid-coated nanocrystals of paclitaxel as dry powder for inhalation: Characterization, in-vitro performance, and pharmacokinetic assessment, Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, Volume 237, 2024, 113865, ISSN 0927-7765, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.113865.
Watch the video below and read more on Vitamin E TPGS here:

