Design of Experiments as a Tool to Optimize the Process of Coating Minitablets with Commercial Gastro-Resistant Coating Mixtures
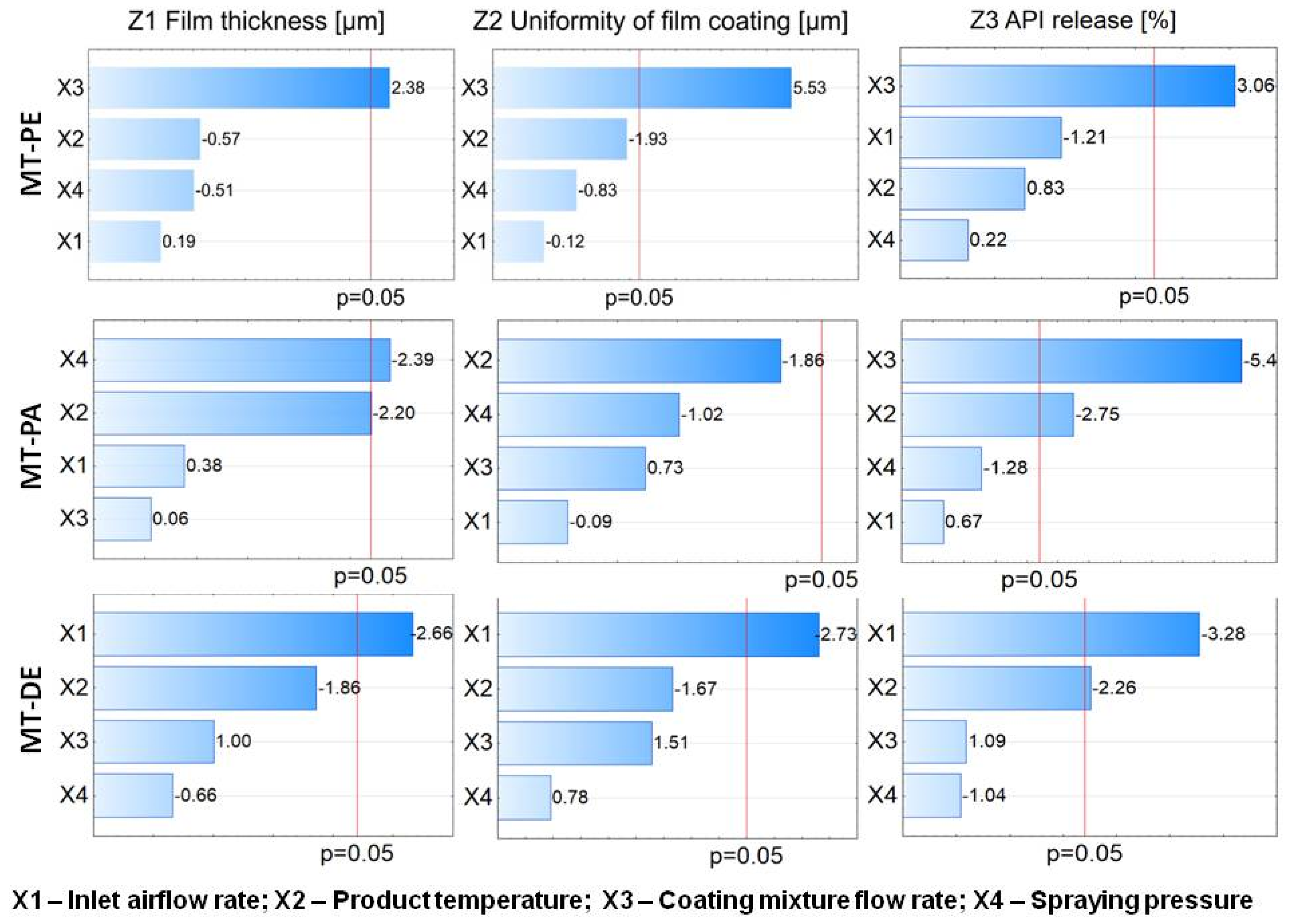
According to the Quality by Design (QbD) concept, Design of Experiment (DoE) was used to indicate critical process parameters and optimize the fluid bed coating of minitablets in a laboratory size batch. Full factorial design was employed to increase knowledge of the process for three kinds of minitablet (MT) cores using two commercial gastro-resistant coating mixtures. The statistical analysis showed that different critical process parameters were indicated for the tested minitablets: X3: the coating mixture flow rate for MTs with pantoprazole sodium and Eudragit L; X2: the product temperature; X3 and X4: the spraying pressure for MTs with pantoprazole sodium and Acryl Eze II; and X1 and X2: MTs with diclofenac sodium. Such differences were the result of features, such as the sub-coat, size, and mass of the cores and the core and coating mixture composition. No optimal parameters were found for any of the tested MT types. Therefore, DoE should be considered as a statistical tool to individually optimize the process for the product, equipment, and tested parameters. However, optimization of the fluid bed coating allowed us to predict the values of the process parameters necessary to obtain good-quality products. Therefore, fluid bed coating may be successfully used to obtain modified-release MTs of high quality after applying the statistical tool DoE.
Download the full article as PDF here Design of Experiments as a Tool to Optimize the Process of Coating Minitablets with Commercial Gastro-Resistant Coating Mixtures
or read it here
Materials
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) were kindly donated as follows: pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate was donated by LEK-AM (Zakroczym, Poland) and diclofenac sodium was donated by Polpharma SA (StarogardGdanski, Poland). Colloidal silicon dioxide: Aerosil 200 (from Evonik, Darmstadt, Germany); crospovidone: Kollidon CLF (from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany); lactose monohydrate: Flowlac 100 and GranuLac 200 (from Meggle, Wasserburg, Germany); microcrystalline cellulose: Avicel PH101 (from Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) and Vivapur PH102 (from JRS Pharma, Rosenberg, Germany); pregelatinized maize starch: Starch 1500 (from Colorcon, Dartford, UK); sodium carbonate (from PPH STANLAB, Lublin, Poland); sodium starch glycolate: Vivastar P (from JRS PHARMA, Rosenberg, Germany); and sodium stearyl fumarate: PRUV (from JRS PHARMA, Rosenberg, Germany) were used to compose the MT cores. The sub-coating was made from hypromellose: Pharmacoat 606 (from Shin-Etsu Chemical, Tokyo, Japan) and polyethylene glycol 6000 (from Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany). A methacrylic acid-ethyl acrylate copolymer was used to obtain the enteric film: Eudragit L 30D55 (from Evonik Industries, Darmstadt, Germany) and the ready-to-use mixture Acryl Eze II (from Colorcon, Dertford, UK). Eudragit was mixed with triethyl citrate (from Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) and talc (from Luzenac VAL Chisone, Porte, Italy).
Frankiewicz, M.; Sznitowska, M. Design of Experiments as a Tool to Optimize the Process of Coating Minitablets with Commercial Gastro-Resistant Coating Mixtures. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1816, https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091816
Read more about Talc here:


