The effect of polymeric binder type and concentration on flow and dissolution properties of SMEDDS loaded mesoporous silica-based granules
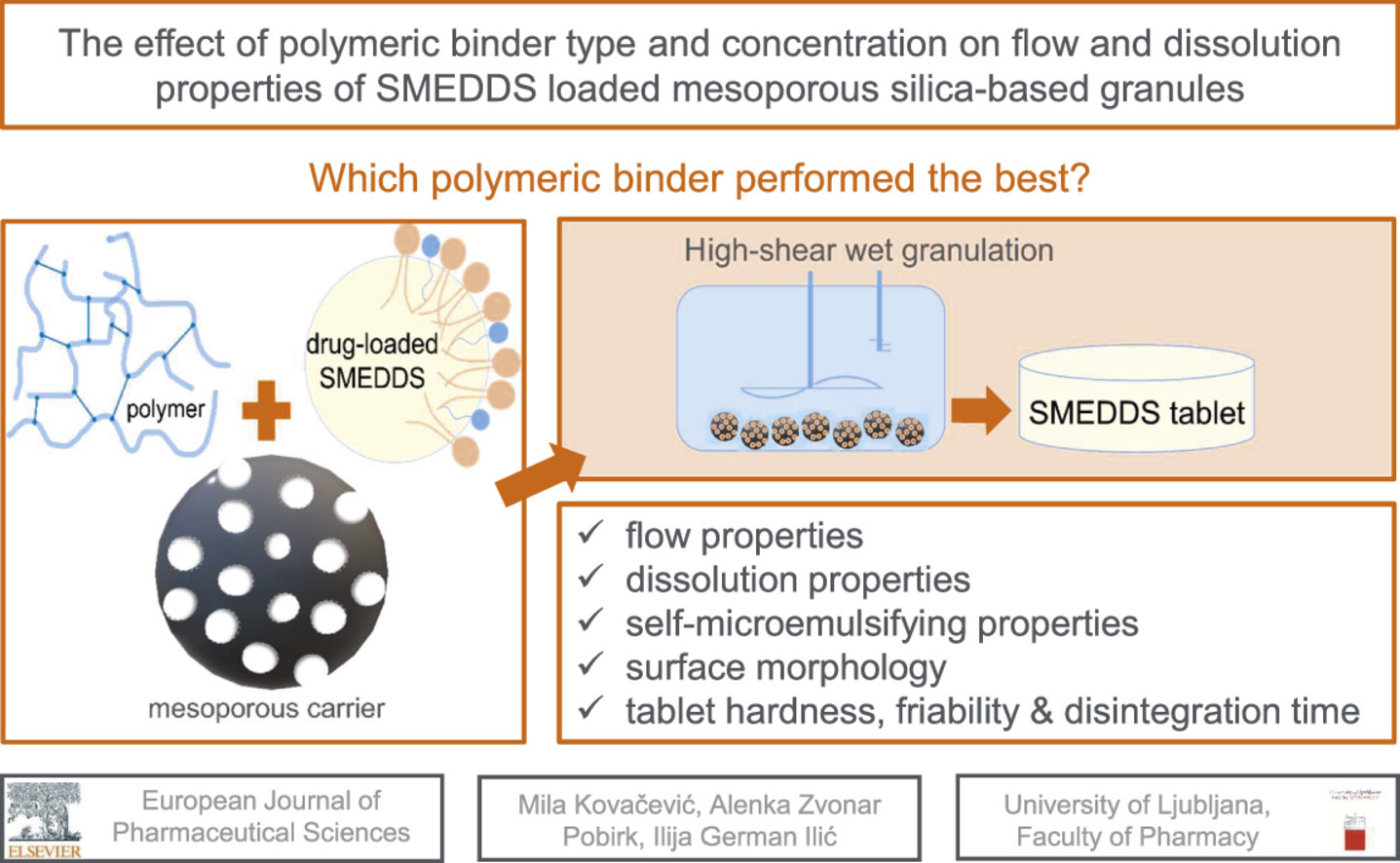
Self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) are lipid-based formulations, designed to improve the solubility of poorly-water soluble drugs. Mesoporous silica is frequently used for SMEDDS solidification by various techniques. One of them is wet granulation, which enables achieving both high SMEDDS load and good flow properties. This study investigated the effect of six polymeric binders’ addition to granulation dispersion (GD) (povidone K30, povidone K90, copovidone, Pharmacoat® 603, Pharmacoat® 615 and MethocelTM K100 Premium LV) on characteristics of produced SMEDDS granules, prepared by wet granulation.
Highlights
Incorporation of higher molecular weight binders results in slower in vitro drug release from solid SMEDDS.
High binder concentration is related to faster in vitro drug release from solid SMEDDS.
Higher binder amount has favorable effect on flow properties, although flowability of all SMEDDS granules is good for further tableting.
Both high-shear granulation and tableting have a (slight) negative effect on drug release rate.
SMEDDS granules and tablets preserved self-microemulsifying properties.
- Povidone K30 is the best polymeric binder candidate for further research.
By incorporation of polymer in GD, it was possible to produce mesoporous silica-based free-flowing granules, with preserved self-microemulsifying properties, responsible for improved in vitro release of carvedilol. The incorporation of higher molecular weight binders resulted in slower in vitro release, while high binder concentration was related to faster drug release. The highest release rate was achieved with povidone K30 at 7.45 % binder concentration, as corresponding granules exhibited complete drug release already in 5 minutes. Granulation method (manual vs. high-shear) influenced the release rate of carvedilol as it was released slower from SMEDDS granules prepared using the granulator.
Finally, SMEDDS tablet formulation was optimized to achieve maximum granule content and adequate tablet hardness. Increased granule content found to negatively influence tablet hardness, as maximum granule content of 25 % was needed to obtain appropriate hardness. Such tablets exhibited short disintegration time, so this final prototype can be considered as orodispersible tablet.
2.1. Materials
Carvedilol (CTX Life Sciences Ltd., Gujarat, India) was used as model drug.
Liquid SMEDDS was composed of mixture of Capmul® MCM EP/NF (mono-diglyceride of medium chain fatty acids, Abitec Corporation, Columbus, Ohio, USA), refined castor oil (Ph. Eur. Grade, Caesar & Loretz GmbH, Hilden, Germany), Kollisolv® PEG E 400 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Luis, MO, USA) and Kolliphor® RH 40 (polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, Sigma-Aldrich, USA). Syloid® 244 FP (silica with average particle size 3.5 μm, Grace GmbH & Co. KG, Worms, Germany) was used as solid mesoporous carrier for liquid SMEDDS.
Different binder types and concentrations were used in GD: PVP K30 (BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany), PVP K90 (BASF, Germany), copovidone VA64 (Kollidon® VA64, BASF, Germany), hypromellose Pharmacoat® 603 (Shin-Etsu Chemical Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), hypromellose Pharmacoat® 615 (Shin-Etsu Chemical Co. Ltd., Japan) and hypromellose MethocelTM K100 Premium LV (DuPont, Wilmington, Delaware, USA).
For SMEDDS tablet production the following materials were used: Kollidon® VA64 as a dry binder, croscarmellose sodium (Ac-Di-Sol®, FMC BioPolymer, Philadelphia, PA, USA) as a disintegrant, microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel® PH 200, FMC Biopolymers, USA) as a filler, and magnesium stearate (Merch KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) as a lubricant and antiadhesive agent.
For preparation of dissolution media, KH2PO4 (Merch KGaA, Germany) HCl (37%, Panreac Quimica S.A.U. Barcelona, Spain), NaOH (Merck KGaA, Germany) and purified water (reverse osmosis, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ljubljana, Slovenia) were used.
Download the full Journal Pre-Proof as PDF here: The effect of polymeric binder type and concentration on flow and dissolution properties of SMEDDS loaded mesoporous silica-based granules – Pre-Proof
or read it here
Mila Kovačević, Alenka Zvonar Pobirk, Ilija German Ilić, The effect of polymeric binder type and concentration on flow and dissolution properties of SMEDDS loaded mesoporous silica-based granules, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2023, 106582, ISSN 0928-0987, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106582.

