Fixed-dose dry powder for inhalation of nintedanib, pirfenidone and mycophenolic acid by thin-film freezing (TFF) technology
Nintedanib and pirfenidone have been approved to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) by delaying progression of the disease. Recently, mycophenolic acid has also been used as an additive treatment for IPF. This study aims to produce and evaluate fixed-dose combinations (i.e., two-drug and three-drug combinations) of nintedanib, pirfenidone, and mycophenolic acid dry powders for inhalation produced by thin-film freezing (TFF). The TFF process, which is a bottom-up particle engineering technology using a rapid freezing process, allows the formation of a homogeneous powder matrix of the fixed-dose combinations of the two or three drugs.
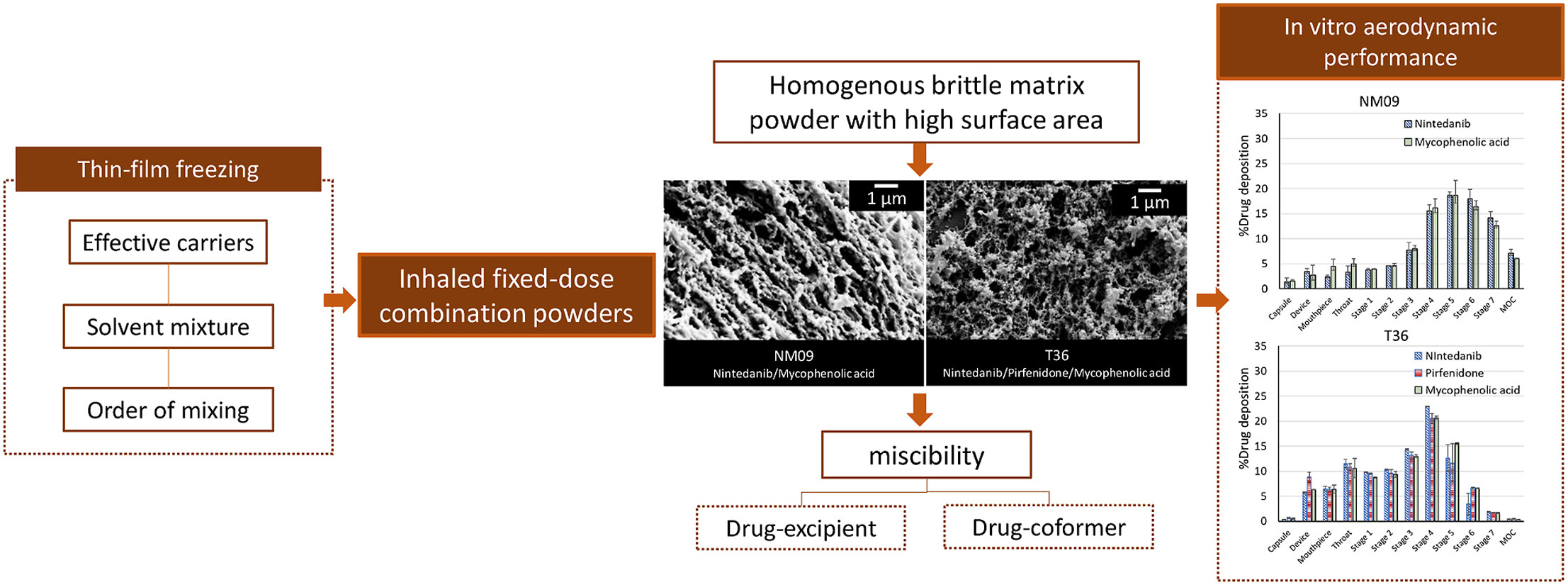
X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) and modulated differential scanning calorimetry (mDSC) confirmed the presence of amorphous nintedanib and crystalline pirfenidone (NIN-PIR), and amorphous nintedanib and amorphous mycophenolic acid (NIN-MPA) in the two-drug combinations. Two-drug formulations of nintedanib and mycophenolic acid prepared by the TFF process exhibited homogenous porous matrix powders with a high surface area and brittle fracture behavior. The in vitro aerodynamic testing of the two-drug combinations demonstrated that nintedanib and mycophenolic acid have similar particle size distributions and high aerodynamic performance of up to 78–82% fine particle fraction (FPF) of the recovered dose.
However, pirfenidone was crystalline in the nintedanib/pirfenidone combinations, resulting in poor aerodynamic performance with FPF (of recovered dose) of 6%–28%. In the three-drug formulations, the TFF process produced a coformer of pirfenidone and mycophenolic acid that prevented pirfenidone crystallization and consequently enhanced aerosolization. Therefore, nintedanib, pirfenidone, and mycophenolic acid exhibited as homogenous brittle matrix powders, resulting in a similar aerodynamic performance with FPF (of recovered dose) of 56%–60%. In conclusion, the fixed-dose combinations produced by the TFF process exhibited drug-excipient miscibility and homogenous brittle matrix powders to enhance aerodynamic performance for inhalation.
Read more here
Materials
The nintedanib (nintedanib esylate) used in this study was purchased from Ontario Chemicals Inc. (Ontario, Canada). The pirfenidone was purchased from Oakwood Products, Inc. (Estill, SC), and the mycophenolic acid was purchased from AK Scientific (CA, USA). The lactose monohydrate and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade acetonitrile were acquired from Fisher Scientific (NJ, USA). The phosphoric acid was acquired from MilliporeSigma (USA), D-Mannitol.
Tuangrat Praphawatvet, Sawittree Sahakijpijarn, Chaeho Moon, Jay I. Peters, Robert O. Williams, Fixed-dose dry powder for inhalation of nintedanib, pirfenidone and mycophenolic acid by thin-film freezing (TFF) technology, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, Volume 85, 2023, 104559, ISSN 1773-2247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104559.
Read more on “Mannitol” here: