Development and characterization of solid lipid-based formulations (sLBFs) of ritonavir utilizing a lipolysis and permeation assay
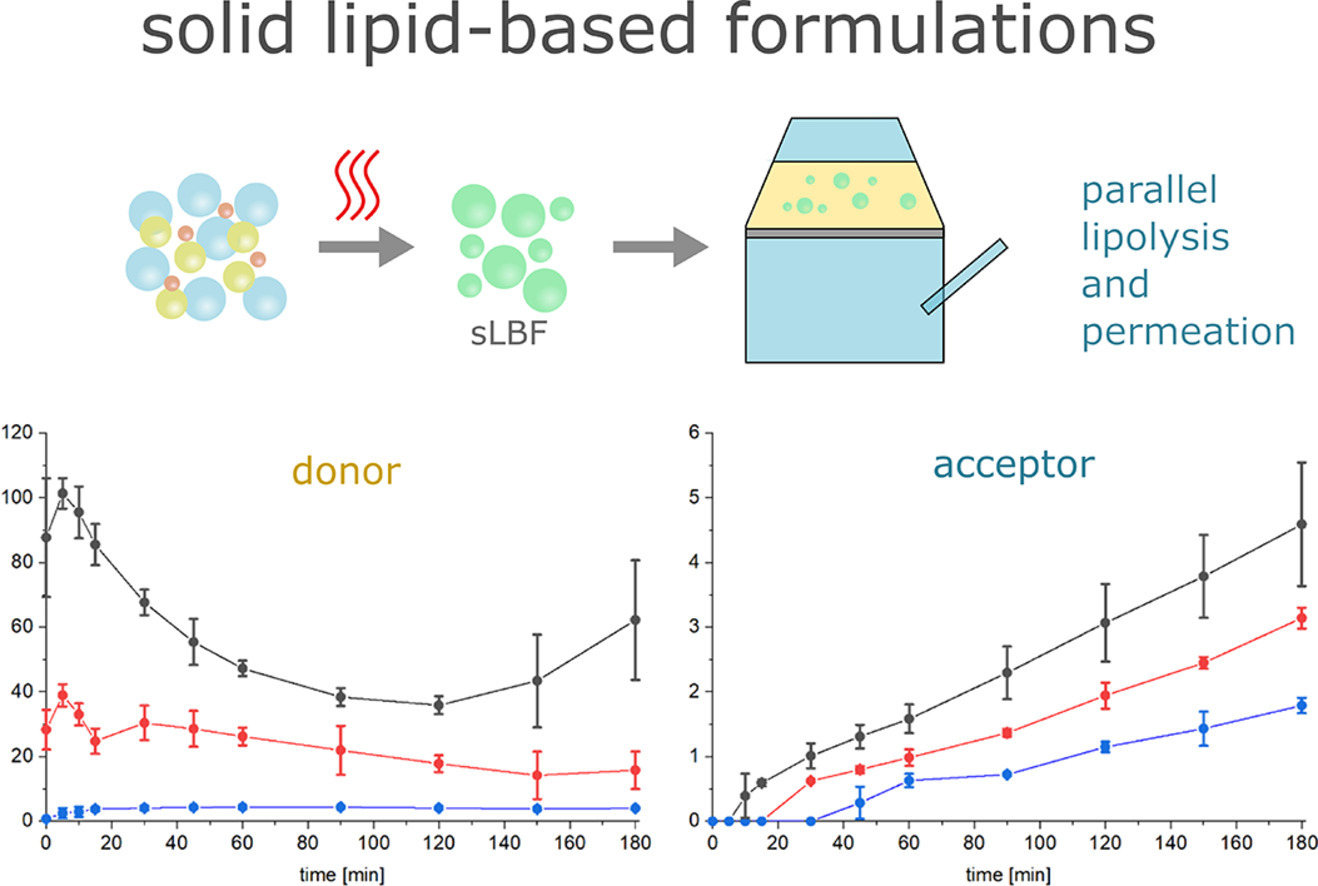
As a high number of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) under development belong to BCS classes II and IV, the need for improving bioavailability is critical. A powerful approach is the use of lipid-based formulations (LBFs) that usually consist of a combination of liquid lipids, cosolvents, and surfactants. In this study, ritonavir loaded solid LBFs (sLBFs) were prepared using solid lipid excipients to investigate whether sLBFs are also capable of improving solubility and permeability. Additionally, the influence of polymeric precipitation inhibitors (PVP-VA and HPMC-AS) on lipolysis triggered supersaturation and precipitation was investigated.
One step intestinal digestion and bicompartmental permeation studies using an artificial lecithin-in-dodecane (LiDo) membrane were performed for each formulation. All formulations presented significantly higher solubility (5 to >20-fold higher) during lipolysis and permeation studies compared to pure ritonavir. In the combined lipolysis-permeation studies, the formulated ritonavir concentration increased 15-fold in the donor compartment and the flux increased up to 71 % as compared to non-formulated ritonavir. The formulation with the highest surfactant concentration showed significantly higher ritonavir solubility compared to the formulation with the highest amount of lipids. However, the precipitation rates were comparable.
The addition of precipitation inhibitors did not influence the lipolytic process and showed no significant benefit over the initial formulations with regards to precipitation. While all tested sLBFs increased the permeation rate, no statistically significant difference was noted between the formulations regardless composition. To conclude, the different release profiles of the formulations were not correlated to the resulting flux through a permeation membrane, further supporting the importance of making use of combined lipolysis-permeation assays when exploring LBFs.
Download the full article as PDF here Development and characterization of solid lipid-based formulations (sLBFs) of ritonavir utilizing a lipolysis and permeation assay
or read it here
Materials
Hard fat (Witepsol® E 85) and glyceryl monostearate (IMWITOR® 491) were kindly donated by IOI Oleo GmbH (Hamburg, Germany). Polyethylene glycol monostearate I (PEG-monostearate, Gelucire® 48/16) was provided by Gattefossé (Saint-Priest, France). Ritonavir (> 99%) was purchased from Shanghai Desano Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone-vinyl-acetate copolymer (Kollidon® VA 64) was kindly donated by BASF (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMC AS, AQOAT® AS MMP) was purchased from Shinetsu (Tokio, Japan). Sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium hydroxide (NaOH) pellets, calcium chloride (CaCl2) granules, phosphate buffered saline (PBS) tablets, Trizma® maleate (TRIS maleate salt), D-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), 4-bromophenylboronic acid (4-BBBA, ≥ 95.0 %), pancreatin from porcine pancreas (8 x USP specifications), Acetonitril (ACN, ≥99.9 %) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, ≥ 99.9 %) were obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Lecithin (L-α-phosphatidylcholine) soy phosphatidylcholine extract (20 %) was purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc. (Alabaster, AL, USA). Ethanol (99.5 %, denatured with isopropyl alcohol) was purchased from Solveco (Rosenberg, Sweden) and n-dodecane (≥99 %) was obtained from Alfa Aesar (Lancashire, UK). Lucifer yellow (LY) CH dilithium salt and FaSSIF/FeSSIF/FaSSGF powder were obtained from Biotium (Fremont, CA, USA) and biorelevant.com (London, UK), respectively. For all experiments, Ultrapure Milli-Q® water (grade I) from a direct water purification system (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was used. The chemical composition and melting points of the main ingredients of the sLBFs are shown in Table 1.
Arne Schulzen, Ioannis I. Andreadis, Christel A.S. Bergström, Julian Quodbach, Development and characterization of solid lipid-based formulations (sLBFs) of ritonavir utilizing a lipolysis and permeation assay, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2024, 106732, ISSN 0928-0987, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106732.

