An Insight into Preparatory Methods and Characterization of Orodispersible Film—A Review
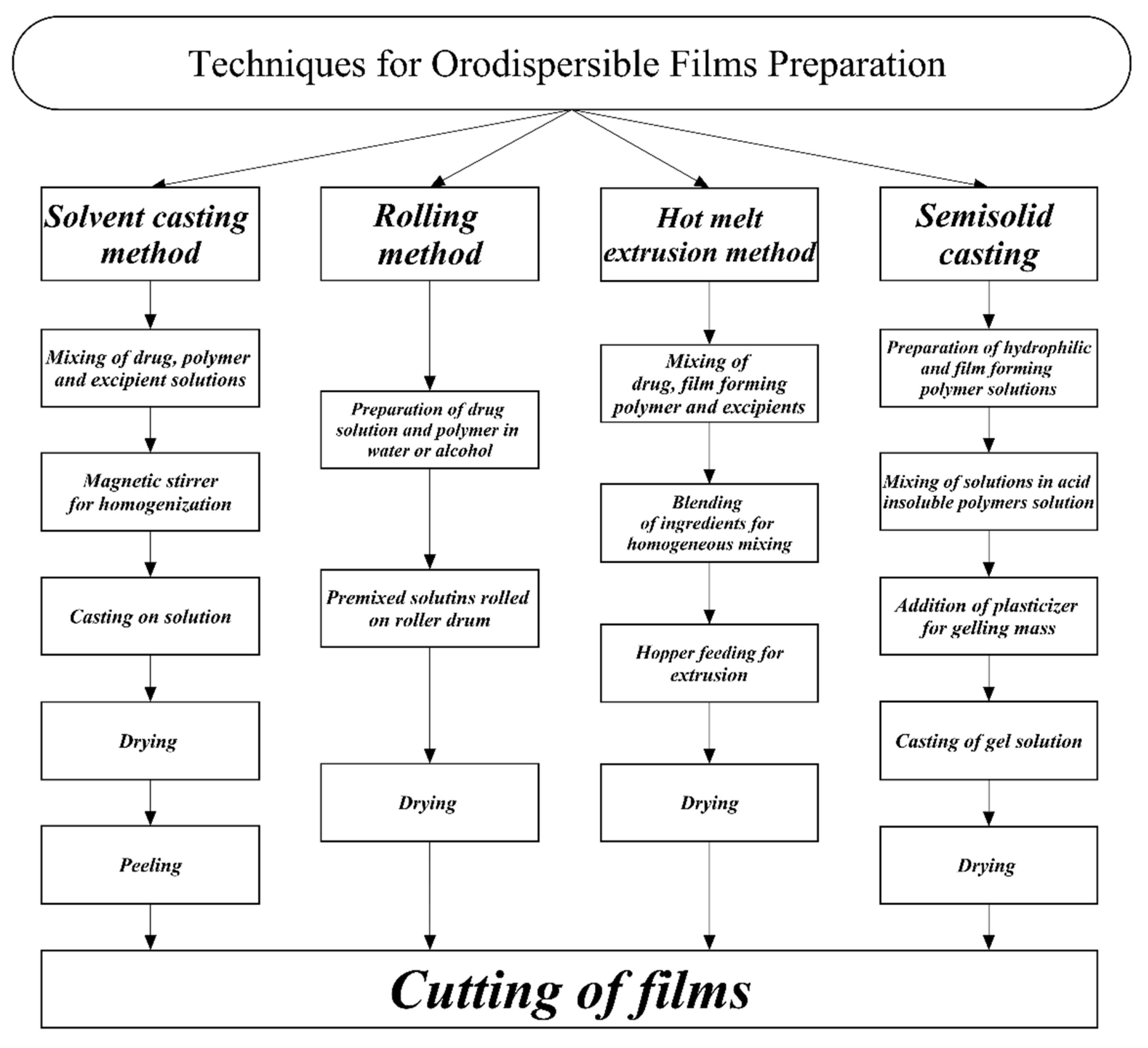
Over the past few decades, researchers and companies have been trying to develop novel drug delivery systems to ensure safety, efficacy, compliance, and patient acceptability. Nowadays drug discovery and development are expensive, complex, and time-consuming processes, but trends are moving toward novel drug delivery systems. This delivery system helps to achieve drug response by local and systemic action through different routes. This novel approach of preparing orodispersible films (ODFs) provides benefits to paediatric, geriatric, and bedridden patients. This review paper aims to provide details on the preparation, characterization, and evaluation of ODFs; it also aims to focus on the positive and negative factors that affect film formulation and give an insight into potential drug candidates and polymers for use in ODFs. ODFs are effective, safe, and have good bioavailability as compared to fast-disintegrating tablets. The novel approach has various advantages because it provides instant effects in emergency situations and in schizophrenic and dysphasic patients without the need for taking water, the films disintegrating within a few seconds in the oral cavity. The solvent casting method is the most frequently used technique to develop ODFs, using film-forming polymers, which have a fast disintegration time, improved drug dissolution, and better drug contents.
Out of all the excipients used in the formulation of ODFs, the film former plays an important role and is one of the key constituents. Maintaining the balance between disintegration times and the mechanical properties of ODFs, polymers, concentrations, and types is the main issue because the properties of polymers are affected by molecular weight. Pullulan, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and cellulose derivatives are the commonest polymers that are used in the preparation of films. Some of the examples of mixtures of polymers used in ODFs are methacrylic acid and Hypromellose, croscarmellose and PVA], and macrogol-PVA and povidone. A class of substances that help to provide flexibility in films are plasticizers, which aid the fabrication of films. In the literature, researchers have studied the impact of plasticizers on ODF preparation, and the selection of type and amount is an important consideration . ODFs or rapidly disintegrating films are prepared with the aim of disintegrating or dissolving in the oral cavity when they are placed on the tongue. Some drugs have bitter tastes, creating a significant challenge in the development of this novel drug delivery system, and taste maskers can also be used as excipients in the preparation of ODFs. Polymers are useful in the development of ODFs and maintain tensile strength. Polymers from natural sources are mostly used in film formulations and are comprehensively cast in OTC films used for sore throat, cough, and breath fresheners. Gums (carrageenan, pectin, and agar) from plant sources can also be used in oral films.
See also Table 4 in the article.
Download the full article as PDF here An Insight into Preparatory Methods and Characterization of Orodispersible Film – A Review
or read it here
Salawi, A. An Insight into Preparatory Methods and Characterization of Orodispersible Film—A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070844

