Lipid based formulations as supersaturating oral delivery systems: from current to future industrial applications
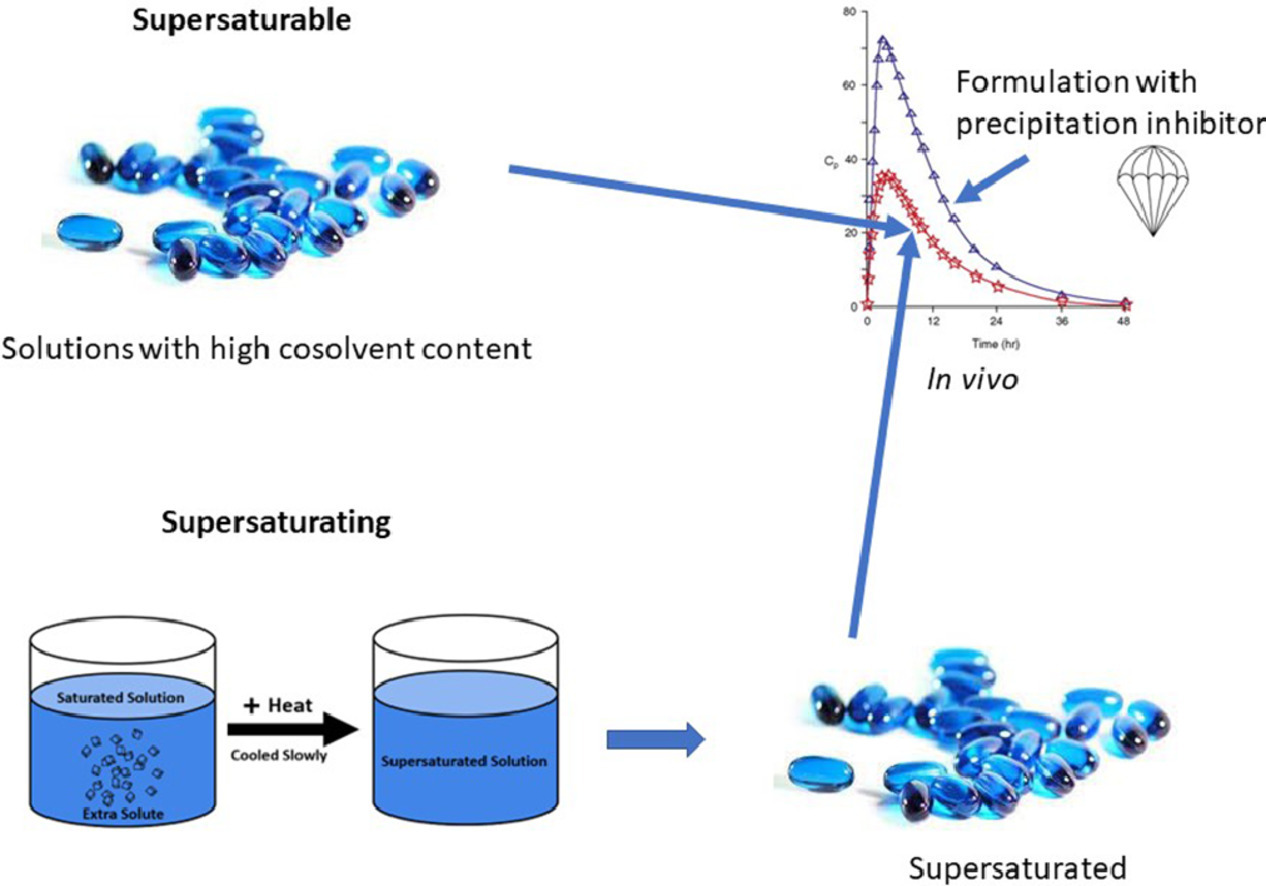
Lipid-based formulations, in particular supersaturated lipid-based formulations, are important delivery approaches when formulating challenging compounds, as especially low water-soluble compounds profit from delivery in a pre-dissolved state. In this article, the classification of lipid-based formulation is described, followed by a detailed discussion of different supersaturated lipid-based formulations and the recent advances reported in the literature. The supersaturated lipid-based formulations discussed include both the in situ forming supersaturated systems as well as the thermally induced supersaturated lipid-based formulations. The in situ forming drug supersaturation by lipid-based formulations has been widely employed and numerous clinically available products are on the market. There are some scientific gaps in the field, but in general there is a good understanding of the mechanisms driving the success of these systems. For thermally induced supersaturation, the technology is not yet fully understood and developed, hence more research is required in this field to explore the formulations beyond preclinical studies and initial clinical trials.
Table 3. Tradenames of lipid excipients, their composition and main function mentioned in the main text or tables.
| Tradename | Potential synonym | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Oils | ||
| Capmul® MCM | Mixture of medium chain mono- and diglycerides | |
| Captex® 300 | Medium chain triglyceride | |
| LabrafacTM lipophile WL1349 | LabrafacTM CC | Medium chain triglyceride |
| Maisine® CC | Maisine® 35-1 | Mixture of long chain mono-, di- and triglycerides |
| Miglyol® 812N | Medium chain triglyceride | |
| PeceolTM | Glyceryl monooleate | |
| Surfactants | ||
| BrijTM L4 | Polyethylene glycol dodecyl ether | |
| Capmul® PG8 | Propylene glycol monocaprylate | |
| Caproyl® 90 | Propylene Glycol Monocaprylate | |
| Gelucure® 44/14 | Lauroyl polyoxyl-32 glycerides | |
| Gelucure® 48/16 | Polyoxyl-32 stearate | |
| Kolliphor® EL | Cremophor EL | PEG-35 hydrogenated castor oil |
| Kolliphor® RH40 | Cremophor RH40 | PEG-40 hydrogenated castor oil |
| Kolliphor® HS15 | Solutol HS15 | Polyoxyl 15 hydrostearate |
| Labrafac® PG | Propylene glycol dicaprolate/dicaprate | |
| Labrafil® M1944CS | Oleoyl polyoxyl-6 glycerides | |
| Labrasol® ALF | Labrasol® | Caprylocaproyl polyoxyl-8 glycerides |
| LauroglycolTM FCC | Propylene glycol monolaurate | |
| Pluronic® F-127 | Poloxamer 407 | 2-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)propoxy]ethanol |
| Polysorbate 80 | Tween 80 | Polyoxyethylene (80) sorbitan monooleate |
| Polysorbate 20 | Tween 20 | Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate |
| Vitamin E-TPGS | D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate | |
| Cosolvents | ||
| PEG | Polyethylenglycol | |
| Tetraglycol | Tetraethylene glycol | |
| Transcutol® P | Transcutol® HP | Diethylene glycol monoethyl ether |
Download the full article as PDF here: Lipid based formulations as supersaturating oral delivery systems: from current to future industrial applications
or read it here
René Holm, Martin Kuentz, Alexandra-Roxana Ilie-Spiridon, Brendan T. Griffin, Lipid based formulations as supersaturating oral delivery systems: from current to future industrial applications, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2023, 106556, ISSN 0928-0987,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106556.

