Self-nano Emulsifying Formulations: An Encouraging Approach for Bioavailability Enhancement and Future Perspective
Abstract
Currently lipid-based formulations are playing a vital and promising role in improving the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Lipid based formulations mainly consist of a drug dissolved in lipids such as triglycerides, glycerides, oils and surface active agent. Self nanoemulsifying formulations (SNEF) are isotropic mixtures of lipids/oils, surfactants and co-surfactants. On mild agitation followed by dilution in aqueous media, such as GI fluids, SNEF can form fine oil-in-water (o/w) nanoemulsions. Present chapter summarizes different types of lipid formulations with special emphasis on SNEF, availability of dosage forms, different components with natural surfactants from medicinal plants, mechanism of SNEF, recent advancements in oral drug delivery, solid SNEDDS, patents on SNEF and future prospects. SNEF emerging as powerful technique to improve solubility and commercialization of solid SNEF is the future novel drug delivery to improve bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs.
Introduction
In recent years, promising efforts have been made to use the potentials of lipid drug delivery systems for solubility and bioavailability enhancement potential. Poorly water-solubility and bioavailability are major challenge in front of formulation of scientists in development of new formulation. Lipid-based drug delivery systems (LBDDS) have great potential of versatility and biocompatibility. Lipid-based formulations modified in different routes to adapt a broad range of products as per the requirements of disease and route of administration. The key factor of LBDDS is their safety and efficacy during design and development of medicines [1]. Recently LBDDS gained much importance in reducing variable food effects and enhancement of bioavailability of poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
Table 1. Commonly used oils in SNEF
| General class | Examples | Commercial name |
| Lipids | Soya lipid, Polyoxy- 35 castor oil | Accutane soft gelatin capsule, Cremophor EL |
| MCTs | Triglycerides of capric acids | Miglyol, Labrafac crodamol, Captex |
| Triace tin | Captex | |
| Medium-chain mono and diglycerides | Capric acids -Mono- and diglycerides | Capmul, Akoline |
| Mono-glycerides (Long-chain) | GMO-Glyceryl monooleate | Maisine, Peceol, GMO-Capmul |
| Polyethylene Glycol (Fatty acids esters) | Polyethylene Glycol monolaurate/dilaurate | Capryol, capmul, Sefsol |
| Polyethylene Glycol dicaprylate/caprate | Lauroglycol, capmule, lauroglycol | |
| Migylol, captex | ||
| Esters fatty acid | Isopropyl myristate | Crodamol EO |
| Fatty acids | Caprylic acid | Crossential |
| Vitamins | Vitamin E D-alpha TocopherylPoly ethylene Glycol1000 Succinate | Tocofersolan |
| (Vit.E-TPGS) |
LBDDS offers great advantages like controlled and targeted drug delivery, stability of developed formulation which is capable of carrying both lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs within it [2]. Lipid formulations classified in to liquid lipid-based formulations, emulsions or microemulsion, Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS), solid-in-oil (S/O) suspension, solid lipid-based formulations, lipid as particulate drug carriers, liposome, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), neosome. Present work gives an overview of Self nano-emulsifying formulations, its components, future perspectives and applications in commercialization. SNEF is the most promising approach which overcomes poor water solubility; bioavailability and formulation difficulties poorly water-soluble drugs [3]. SNEF designed to increase solubility and bioavailability of drugs belonging to the BCS Class II-IV.
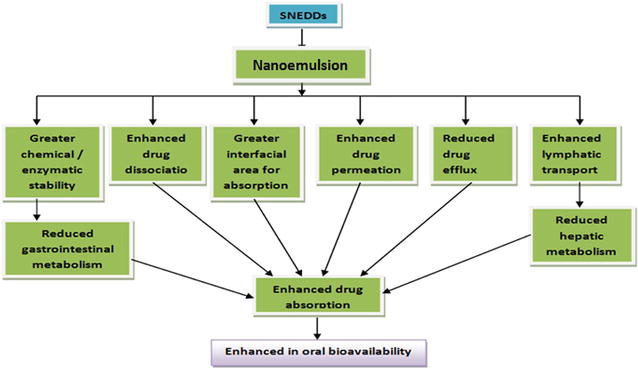
SNEF comprehensively enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs (PWSDs) by micelle formation. In SNEF API introduced as nanosized oil droplets. Rapid drug release of SNEF in the stomach due to the generation of nanosized oil droplets leads to the quick onset of action in the GI tract. SNEF easily dispersible due to the partitioning of a drug between oil and water which generates a larger interfacial area. SNEF offers ample of advantages such as reproducible plasma drug conc., decrease in variability of rate and extent of absorption [4]. SNEF holds the drug in a solution that allows enough time for drug absorption through GIT [5].
Table 2. Commonly used surfactants in SNEF
| General class | Examples | Commercial name |
|---|---|---|
| Polysorbates | Sorbitan monolaurate | Tween 80, crillet 4 |
| Sorbitan esters | Sorbitan monolaurate | Span 20,68,80, Crill 1,3,4 |
| Copolymers | Poloxamer 188 and 407 | Pluronic F-68 and F 127 |
| Castor oil | Castor oil | Cremphor, Etocas |
| Polyglycolyzed glycerides | Linoleoyl macrogol glycerides Oleoyl macrogol glycerides Caprylocapryol macrogol glycerides Polyglyceryl oleate Lauroyl macrogol glycerides Stearoyl macrogyl glycerides |
Labrafil, Labrasol, Plurol oleique, Gelucire, Gelucire |
| Phospholipids | Soybean / sunflower lecithin | ALCOLEC® |
Read more
Sunil T. Galatage, Rahul Trivedi, Durgacharan A. Bhagwat, Arehalli S. Manjappa, Swapnil S. Harale, Abhinandan A. Alman, Swapnil S. Chopade, Sujit A. Desai, Shashikant Adsule, Ashish M. Phutane, Samruddhi S. Kadam, Shruti R. Mandekar, Amruta M. Chougale, Krushnabai R. Margale, Rohini M. Patil, Shweta N. Kalebere and Amolkumar A. Kempwade, Submitted: October 12th, 2021 Reviewed: October 21st, 2022 Published: December 1st, 2022, DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.108703

